What is the access time to RAM. What is RAM for? RAM in modern systems

RAM is a special microcircuit used to store all kinds of data. There are many varieties of these devices, they are produced by various companies. The best producers are most often of Japanese origin.
What is it and what is it for?
RAM (the so-called RAM memory) is a type of volatile microcircuit used to store all kinds of information. Most often it contains:
- machine code of programs currently executing (or in standby mode);
- input and output data.
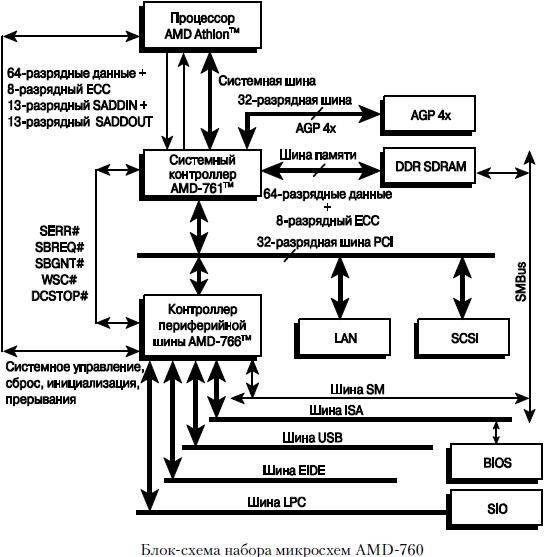
Data exchange between the central processor and RAM is carried out in two ways:
- using ultra-fast ALU register;
- through a special cache (if available in the design);
- directly (directly via the data bus).
The devices under consideration are circuits based on semiconductors. All information stored in all kinds of electronic components, remains accessible only when electric current is present. As soon as the voltage is turned off completely, or a short-term power cut occurs, then everything that was contained inside the RAM is erased or destroyed. ROM devices are an alternative.
Types and amount of memory
The board today can have a volume of several tens of gigabytes. Modern technical means allow you to use it as quickly as possible. Most operating systems are equipped with the ability to interact with such devices. There is a proportional relationship between the amount of RAM and the cost. The larger its size, the more expensive it is. And vice versa.

Also, the considered devices may have different frequencies. This parameter determines how quickly the interaction between RAM and other PC devices (CPU, data bus and video card) is carried out. The higher the operating speed, the more operations the PC will perform per unit of time.
The value of this characteristic also directly affects the cost of the device in question. The modern fastest modification can "memorize" 128 GB. It is produced by a company called Hynix and has the following performance characteristics:

All modern RAM can be divided into two types:
- static;
- dynamic.
Static type
More expensive today is the static microcircuit. It is marked as SDRAM. Dynamic is cheaper.
The distinctive features of the SDRAM version are:

Also, a distinctive feature of RAM is the ability to select the bit to which any information will be recorded.
The disadvantages include:
- low recording density;
- relatively high cost.
Devices random access memory computers of all kinds (SDRAM and DRAM) have external differences. They are contained in the length of the contact part. Its shape also differs. The designation of the RAM is located both on the sticker label and printed directly on the strap itself.
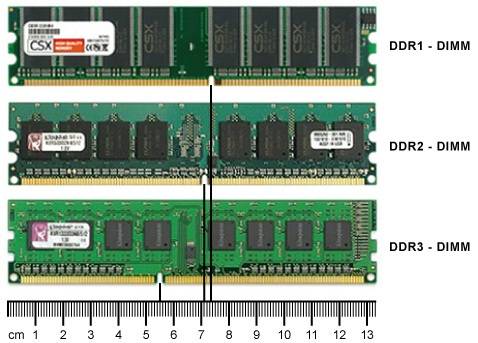
There are many different SDRAM modifications available today. It is designated as:
- DDR 2;
- DDR 3;
- DDR 4.
Dynamic type
Another type of microcircuit is designated as DRAM. It is also completely volatile, and the write bits are accessed in an arbitrary manner. This type is widely used in most modern PCs. It is also used in those computer systems where latency requirements are high - DRAM performance is an order of magnitude higher than SDRAM.

Most often, this type has a form factor of the DIMM type. The same design solution is used for the manufacture of the static circuit (SDRAM). The peculiarity of the DIMM version is that there are contacts on both sides of the surface.
OP parameters
The main criteria for choosing microcircuits of this type are their operating parameters.
You should focus primarily on the following points:
- frequency of work;
- timings;
- voltage.
They all depend on the type of a particular model. For example, DDR 2 will perform various actions definitely faster than the DDR 1 bar. Since it has more outstanding performance characteristics.
Timing is the time delay of information between different components of the device. There are quite a few types of timings, all of them directly affect performance. Small timings allow you to increase the speed of various operations. There is one unpleasant proportional relationship - the higher the speed of the random access memory, the higher the timings.
The way out of this situation is to increase the operating voltage - the higher it is, the less timings become. The number of operations performed per unit of time increases at the same time.
Frequency and speed
The higher the RAM bandwidth, the higher its speed. Frequency is a parameter that determines the bandwidth of the channels through which various kinds of data are transferred to the CPU through the motherboard.
It is desirable that this characteristic coincides with the permissible speed of the motherboard.
For example, if the bracket supports 1600 MHz, and the motherboard does not exceed 1066 MHz, then the speed of data exchange between the RAM and the CPU will be limited by the capabilities of the motherboard. That is, the speed will be no more than 1066 MHz.
Performance
Performance depends on many factors. The number of planks used has a very large effect on this parameter. Dual-channel RAM works an order of magnitude faster than single-channel RAM. The ability to support multichannel modes is indicated on a sticker located over the board.
These designations are as follows:

To determine which mode is optimal for a particular motherboard, it is necessary to calculate the total number of slots for connection and divide them by two. For example, if there are 4 of them, then you need 2 identical strips from the same manufacturer. When installed in parallel, the Dual mode is activated.
Working principle and functions
The operation of the OP is implemented quite simply, writing or reading data is carried out as follows:
- an electrical signal is applied to the required line;
- the transistor opens;
- the electrical charge present in the capacitor is applied to the desired column.

- executable libraries;
- key codes, which were pressed;
- results of various mathematical operations.
- Kingston;
- Hynix;
- Corsair;
- Kingmax.
- Samsung.
- OS: Windows 8.1;
- CPU: i5-4670K;
- video card: GeForce GTX 780 Ti;
- motherboard: LGA1150, Intel Z87.
Each column is connected to an extremely sensitive amplifier. It registers the flow of electrons that occur when the capacitor is discharged. In this case, the corresponding command is given. Thus, access to the various cells located on the board takes place. There is one important nuance that you should definitely know. When served electrical impulse to any line, it opens all its transistors. They are directly connected to it.
From this we can conclude that one line is the minimum amount of information that can be read when accessing. The main purpose of RAM is to store various kinds of temporary data that are needed while the personal computer is turned on and the operating system is functioning. The most important executable files are loaded into RAM, the CPU executes them directly, just saving the results of the operations performed.
The cells also store:
If necessary, everything that is in RAM can be saved to the hard disk by the central processor. And to do it in the form in which it is necessary.
Manufacturers
In stores, you can find a huge amount of RAM from a variety of manufacturers. A large number of such products began to be supplied from Chinese companies.

To date, the most productive and high-quality products are the following brands:
It is a compromise between quality and performance.
RAM characteristics table
The same type of RAM from different manufacturers has similar performance characteristics.
That is why it is correct to carry out comparison, taking into account only the type:
DDR
DDR2
DDR3
frequency range
100-400
400-800
800-1600
Working voltage
2.5v +/- 0.1V
1.8V +/- 0.1V
1.5V +/- 0.075V
Number of blocks
4
4
8
Termination
limited
limited
all DQ signals
Topology
TSOP
TSOP or Fly-by
Fly-by
Control method
-
OCD
Automatic calibration with ZQ
Temperature sensor
Not
Not
Yes
Performance and price comparison
The performance of RAM directly depends on its cost. You can find out how much a DDR3 module costs in your nearest computer store, and you should also familiarize yourself with the price of DDR 1. Comparing their operating parameters and price, and then testing, you can easily verify this.

It is most correct to compare RAM of the same type, but with different performance, depending on the operating frequency:
A type
Operating frequency, MHz
Cost, rub.
Speedwork, Aida 64,Memory Read, MB / s
DDR 3
1333
3190
19501
DDR 3
1600
3590
22436
DDR 3
1866
4134
26384
DDR 3
2133
4570
30242
DDR 3
2400
6548
33813
DDR 3
2666
8234
31012
DDR 3
2933
9550
28930
In Aida 64, all DDR 3 tests were performed on identical hardware:
RAM is a very important part of a PC and greatly affects its performance. That is why, to increase it, it is recommended to install strips with high frequency and small timings. This will give a big boost in computer performance, it is especially important for games and various professional programs.
A lot of computer users often ask themselves what is RAM. To help our readers understand RAM in detail, we have prepared a material in which we will consider in detail where it is can be used and what his types are now used. We will also look at a little theory, after which you will understand what modern memory is.
A bit of theory
The abbreviation for RAM stands for - random access memory... Basically, it is the RAM that is primarily used in your computers. The principle of operation of any type of RAM is built on storing information in special electronic cells... Each of the cells has a size of 1 byte, that is, it can store eight bits of information. Each electronic cell has a special address... This address is needed in order to be able to access a specific electronic cell, read and write its contents.
Also, reading and writing to an electronic cell must be carried out at any time. In the English version, RAM is RAM... If we decipher the acronym RAM (Random Access Memory) - random access memory, then it becomes clear why reading and writing to a cell is carried out at any time.
Information is stored and rewritten in electronic cells only when your PC works, after turning it off, all the information that is in RAM is erased. The set of electronic cells in modern RAM can reach a volume of 1 GB to 32 GB. The types of RAM that are currently in use are called DRAM and SRAM.
- First, DRAM is dynamic random access memory, which consists of capacitors and transistors... Information storage in DRAM is due to the presence or absence of charge on the capacitor (1 bit of information), which is formed on the semiconductor crystal. To store information, this type of memory requires regeneration... Therefore this slow and cheap memory.
- Second, SRAM is Static RAM... The principle of accessing cells in SRAM is based on a static flip-flop that includes several transistors. SRAM is expensive memory, so it is mainly used in microcontrollers and integrated circuits, which have little memory. it fast memory, not requiring regeneration.
Classification and types of SDRAM in modern computers
The most common type of DRAM memory is synchronous memory SDRAM... The first subtype of SDRAM is DDR SDRAM. DDR SDRAM memory modules appeared in the late 1990s. At that time, computers based on Pentium processes were popular. The image below shows a 512 MB DDR PC-3200 SODIMM bar from GOODRAM.
Prefix SODIMM means memory is for laptop... In 2003, DDR SDRAM was replaced by DDR2 SDRAM... This memory was used in modern computers of that time until 2010, when it was supplanted by the next generation of memory. The image below shows a 2 GB DDR2 PC2-6400 bracket from GOODRAM. Each generation of memory demonstrates an ever increasing data exchange rate.
DDR2 SDRAM was replaced in 2007 by an even faster DDR3 SDRAM... This format remains the most popular to this day, although a new format breathes in its back. The DDR3 SDRAM format is now used not only in modern computers, but also in smartphones, tablet pc and budget graphics cards... Also, DDR3 SDRAM is used in the game console Xbox one eighth generation from Microsoft. This set-top box uses 8 gigabytes of DDR3 SDRAM RAM. The image below shows 4GB DDR3 PC3-10600 memory from GOODRAM.
DDR3 SDRAM memory type will be replaced by a new type soon DDR4 SDRAM... After that, DDR3 SDRAM is waiting for the fate of past generations. Mass memory release DDR4 SDRAM started in Q2 2014 and is already being used on motherboards with a cpu socket Socket 1151... The image below shows the format bar DDR4 PC4-17000 4 gigabytes from GOODRAM.
DDR4 SDRAM bandwidth can be up to 25 600 Mb / s.
How to determine the type of RAM in a computer
It is very easy to determine the type of RAM that is in a laptop or a stationary computer using the utility CPU-Z... This utility is completely free. Download CPU-Z can be obtained from its official website www.cpuid.com. After downloading and installing, open the utility and go to the " SPD". The image below shows the utility window with the " SPD».

In this window, you can see that the computer on which the utility is open has RAM of the type DDR3 PC3-12800 4 gigabytes from Kingston. In the same way, you can determine the type of memory and its properties on any computer. For example, below is a window CPU-Z with RAM DDR2 PC2-5300 512 GB from Samsung.

And this window shows a window CPU-Z with RAM DDR4 PC4-21300 4 GB from ADATA Technology.

This method of checking is simply irreplaceable in a situation when you need to check for compatibility the memory you are about to purchase for rAM expansion your PC.
We select the RAM for the new system manager
In order to select RAM for a specific computer configuration, we will describe an example below, which shows how easy it is to match RAM to any PC configuration. For example, we will take this latest Intel processor-based configuration:
- CPU - Intel Core i7-6700K;
- Motherboard - ASRock H110M-HDS on Intel H110 chipset;
- Video card - GIGABYTE GeForce GTX 980 Ti 6GB GDDR5;
- SSD - Kingston SSDNow KC400 1000 GB;
- Power Supply - Chieftec A-135 APS-1000C 1000W.
To select the RAM for such a configuration, you need to go to the official page of the ASRock H110M-HDS motherboard - www.asrock.com/mb/Intel/H110M-HDS.
The page contains the line “ Supports DDR4 2133", Which says that a 2133 MHz RAM is suitable for the motherboard. Now let's go to the menu item " Specifications" on this page.
In the page that opens, you can find the line “ Max. capacity of system memory: 32GB”, Which states that our motherboard supports up to 32 gigabytes of RAM. From the data that we received on the motherboard page, we can conclude that this type of RAM would be an acceptable option for our system - two DDR4-2133 16 GB PC4-17000 memory modules.
We specifically indicated two 16 GB memory modules, and not one 32, since two modules can work in dual channel mode.
You can install the above modules from any manufacturer, but these RAM modules will work best. They are presented on the official page for the motherboard in the paragraph " Memory Support List", As their compatibility has been verified by the manufacturer.
The example shows how easy it is to find out information about the system unit in question. In the same way, RAM is selected for all other computer configurations. I would also like to note that on the configuration discussed above, you can run all newest games with the highest graphics settings.
For example, on this configuration, new games such as Tom clancy's the division, Far cry primal, Fallout 4 and many others, since such a system meets all the realities of the gaming market. The only limitation for such a configuration would be its price... The approximate price of such a system unit without a monitor, including two memory modules, a case and components described above, will be about 2000 dollars.
Classification and types of SDRAM in video cards
Newer graphics cards and older models use the same type of synchronous SDRAM. In new and outdated models of video cards, this type of video memory is most often used:
- GDDR2 SDRAM - up to 9.6 GB / s bandwidth;
- GDDR3 SDRAM - up to 156.6 GB / s bandwidth;
- GDDR5 SDRAM - up to 370 GB / s bandwidth.
To find out the type of your video card, the amount of its RAM and the type of memory, you need to use a free utility GPU-Z... For example, the image below shows the program window GPU-Z, which describes the characteristics of the video card GeForce GTX 980 Ti.

The popular today GDDR5 SDRAM will be replaced in the near future by GDDR5X SDRAM... This new video memory classification promises to raise bandwidth to 512 GB / s... The answer to the question of what manufacturers want to achieve from such a large throughput is quite simple. With the advent of formats such as 4K and 8K, as well as VR devices, the performance of current video cards is no longer enough.
Difference between RAM and ROM
ROM stands for read-only storage... Unlike random access memory, ROM is used to record information that will be stored there permanently. For example, ROM is used in such devices:
- Mobile phones;
- Smartphones;
- Microcontrollers;
- BIOS ROM;
- Various household electronic devices.
In all the devices described above, the code for their operation is stored in ROM. ROM is an non-volatile memory, therefore, after turning off these devices, all information will be saved in it - which means this is the main difference between ROM and RAM.
Summing up
In this article, we briefly learned all the details, both in theory and in practice, concerning random access memory and their classification, and also considered what is the difference between RAM and ROM.
Also, our material will be especially useful for those PC users who want to know their type of RAM installed in the computer, or find out which rAM needs to be applied for different configurations.
We hope our material will be interesting for our readers and will allow them to solve many problems related to RAM.
Related Videos
This phrase is quite popular - random access memory. Many people have heard about it and sometimes seen errors in the system associated with it, as well as write about it on many sites if you want to download a program or game. In this article you will learn almost everything you need and everything connected with it. I hope after reading there will be no more questions and you will become more literate.
I'll start, perhaps, from afar ...
What is RAM?
RAM is a bar in or, etc.
It turns out that if you disassemble the system unit (I will focus on the PC in the article, because it is easier there), then you can visually see this bar (and sometimes there are several of them) and this is correct. It looks something like this:

in a laptop like this:

Thus, RAM is one of the "parts" of the computer. Moreover, one of the main ones, without which the computer will not even boot.
By the way, RAM is also often called RAM, memory, RAM (Random Access Memory), RAM, etc.
What is RAM for?
To understand this, you need to pay attention to the first word.
The fact is that when the "brain" of a computer (central processor) accesses data on (and it accesses them almost constantly, because everything is stored there), then it does it through an intermediary - our RAM.
The operating system acts as a kind of intermediary or buffer. When the processor needs something, it sends a command to RAM, and it already copies information from the hard disk. Then the processor works only with the RAM, and when it finishes, the data is copied back to the hard drive.
Perhaps you will have a question "So why is everything so complicated? Why use the RAM if you can directly or can handle it yourself?" The thing is that the hard drive only stores information, and if the processor also loaded it with the fact that it would be necessary to work with it, then it would become terribly slow. Do we need it? Nope.
By the way, there is such a thing as Virtual Memory and Paging File. You can read in more detail in the article.
In short, I will only write that when there is little space left in the RAM (it constantly stores something in itself and new processes are still being performed), then it still turns to the hard disk (well, where to go ...) and takes away from there a place. The truth from this can slow down the computer.
Thus, some data is always stored in RAM. It can be the results of your actions in, and, and in, and in general, everything is always "done" through RAM, as through an intermediary.
Here you should also know that the information is copied from the hard disk to the RAM, then changes in it, and then again sent to the hard disk. The simplest and most common example of this is how you work with text documents.
You open it first, then modify it, and then save and close (or close with save). Do you understand what I'm driving at? Yes Yes. You have worked with a document in RAM, and then you need to rewrite it, because there is only an unmodified copy on disk.
By the way, that is why, in the event of a failure and an emergency shutdown of the computer, you risk losing, in most cases, not saved data. Just those that are currently in the RAM.
Types of RAM
As I wrote above, RAM is a special module that is built into a special connector in the motherboard. You can see how it looks in the first picture above.
Of course, progress does not stand still. Today, you can find a hard disk that contains its own high-speed buffer to increase the speed of reading / writing information. There are also such video cards with the same principle. Likewise, the "strips" of RAM themselves can be equipped with special heatsinks to ensure the best heat transfer, which therefore affects performance.
But back to types ... Now there are only two types - these are statistical and dynamic.
Statistical type of random access memory (SRAM (Static random access memory)) is created on the basis of semiconductor triggers and has a very high speed of operation. It has two disadvantages: high cost and takes up a lot of space. Therefore, in desktop computers, and indeed in everyday life, does not occur.
Dynamic type of RAM (DRAM (Dynamic random access memory)) is based on capacitors, therefore it has a high recording density and a relatively low cost. The disadvantages arise from the peculiarities of its design, namely, the use of small capacitors leads to a rapid self-discharge of the latter, so their charge has to be periodically replenished. This process is called memory regeneration, hence the name dynamic memory. Regeneration noticeably slows down the speed of its operation, therefore, various intelligent circuits are used to reduce time delays.
Dynamic memory is also split across generations. I will not go into history too much, I will only write that the third generation is now widespread DDR3 SDRAM, which replaced DDR2 (they are even still found on old computers to this day) and they are preparing to replace them DDR4 (that's just not too soon I will think).
RAM size
It is the main unit of measurement for RAM and is often used. Measured in megabytes (MB) and gigabytes (GB).
The most common question is How much RAM to use? It all depends on two things:
1)
from what you will be doing. For example, to access the Internet and the simplest work on a computer, 1GB may well be enough. But it's better to take with a margin and put at least 2 GB.
If you want to play games and engage in graphics, then bet 4 GB or more.
I have enough 4 GB for everything. So my advice is 4GB of RAM and everything will be fine.
2)
from the bitness of your operating system. We read the article.
In short, I'll just write that if 32x, then no more than 4x. If 64x, then as much as necessary.
Much also depends on yours, in particular on the number and type of connectors for the RAM. Of course, you need to have enough connectors and fit the type.
How to find out the RAM of your computer
To see what kind of RAM you have, you can use two ways.
1)
Turn off the computer, open the system unit and remove the RAM bar. Next, we look at the sticker (sticker) on it and everything will be written there - both the type and frequency and other information.
If it is not there, then at least from the picture determine the type:

2) Through a well-known utility CPU-Zwhich can be downloaded from. In the tab Memory you can check basic information such as type (Type), size (Size), mode of operation and used timings:

On the SPD tab, you can see all the characteristics of a specific memory module installed in the selected slot:

I would also like to write about the SPD tab that it contains information from the chip of the same name in the RAM. The manufacturer writes in it all information about it (volume, marking, manufacturer, serial number, recommended delays, etc.) and when the system boots, the computer reads all this information and sets the memory operation mode, in connection with the settings contained in the chip.
How to clear RAM
As I wrote above, the RAM is loaded more and more during the operation of the computer. If its volume is small, then it may be such that the computer will start to slow down. Therefore, you should clear the RAM and then the computer will stop slowing down.
For cleaning, you can use the following methods:
1) Close unnecessary programs.
2) Wait a little. Windows has a utility for cleaning the RAM. True, it doesn't always work.
3) Take advantage of special programs. I will not describe them, I will only write links to official sites:
4) Reboot
How to increase RAM
I think everything is very simple here. You cannot increase it programmatically, only physically.
You just need to purchase the desired bar. And which one is needed? Read about it where it was written about the volume.
I just want to add here that if you already have one 2 GB stick, and you want 4, then it is better to take another one for 2 and so that they work in parallel. Then they will have a multi-thread and they will be faster if you pull one by 2 and put 4 instead.
Better to use in pairs.
That's all I think. If you haven't written anything about RAM or what is not clear - write in the comments.
And again everyone, hello! Today we will focus on RAM. What is RAM? What is it for? How it works? What types of RAM are there? What characteristics should you pay attention to when choosing it? You will find answers to these questions below in this article. And let's start in order.
What is RAM?
Random access memory - it is RAM (Random Access Memory), RAM (random access memory), memory, RAM is a volatile part of the computer memory system, in which the executable machine code (programs), as well as input, output and intermediate data processed by the processor.
Physically, the RAM module is embodied in the form of such strips, which are inserted into a special connector on:

Here, in principle, I answered the first two questions. Although no, from this definition, little is clear to the average person. But now we will analyze everything in detail. So.
There are several types of memory in a computer: energy NOTdependent and volatile or temporary.
Nonvolatile memory is any memory device that can store data, whether powered or not. In a computer, this is. You can save a file to it, unplug your computer, and the next time you plug it back in, everything will stay in place.
Volatile memory is computer memory that requires constant power to store information. That in a computer is the RAM. Which means that if you turn off the power from it (turn off the computer), all the information stored in it will disappear. That is, every time you turn on your computer, its RAM is empty.
I think this is understandable. The next part of the definition answers our next question.
What is RAM for?
The question will be fair: why in a computer, besides a hard disk, on which data is stored, regardless of whether it is powered or not, is there an additional, such an unreliable thing as RAM?
The fact is that in comparison with the speed of work, the speed of reading and writing to a hard disk is very low. And if the processor worked directly with it, the computer's performance would be very low.
The RAM, in comparison with the hard disk, works much faster. Apart from the various caches, RAM will be the fastest element in a computer device, after the central processor.
Thus, RAM is needed to increase the performance of the computer, due to the fact that it allows the latter to get the necessary data faster.
How does it all work?
When you start the computer, all the necessary data: the operating system kernel, drivers, various services and autorun programs are loaded from the hard disk into RAM and from there the CPU takes them for processing. The processor also returns the results of its work to the RAM and not to the hard disk. Every program, every window of any program you open on your computer is in RAM. The central processor works with it. And only when you save some results of your work, they are written to the hard disk.
To help you understand better, let's look at a simple example of creating a text document in Word.
When you click on the shortcut to launch the program, all the files necessary for its operation are loaded into RAM, and after that the editor window appears on the computer monitor. When you start writing text, it is also in RAM, you just won't find it on your hard drive. In order for the result of your work to be saved on it, it must be saved by clicking the button of the same name in Word. Everyone at least once had such a thing that you write, write some text and suddenly closed the program or the computer turned off, and after turning it on again, your text disappeared. Precisely because the RAM has gone to zero, and you have never bothered to preserve your creativity.
I think now you already understand what RAM is, why it is needed and how it works. Now let's move on to more practical things. Namely, we will consider the types of random access memory and its main characteristics.
Types (types) of random access memory
Nowadays, random access memory can be of two types: static (SRAM) and dynamic (DRAM). Static RAM compared to dynamic RAM is faster due to its production technology, but at the same time, it is more expensive. This type is often used as a processor cache. DRAM technology is used for mass production of RAM modules. And there are several types of such memory. Those that can now be found:
- DDR SDRAM - synchronous dynamic memory with random access and double data rate ( Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) of the first generation;
- DDR2 SDRAM - second generation DDR SDRAM;
- DDR3 SDRAM - third generation DDR SDRAM;
- DDR4 SDRAM - fourth generation DDR SDRAM;
As you might guess, DDR SDRAM is the oldest type of RAM, which is very difficult to find now. DDR4 is the newest. DDR3 is by far the most common. These types of memory differ among themselves in performance and appearance.
In order to prevent accidentally inserting a strap with one type of RAM into a slot intended for a different type, there is a special key (cut) on the strap, and a protrusion in the connector on the motherboard in the same place. And each type of memory is different.

Also, with this key you will not be able to insert the RAM module in reverse.
Main characteristics of RAM
- RAM type... You should know what type of RAM your motherboard supports: DDR, DDR2, DDR3 or DDR4. And already from this start further.
- RAM size... Here you need to build on your needs. As I wrote above, all running programs will fit into RAM. Accordingly, the more RAM you have on your computer, the more programs you can use at the same time. But still I will give you a little hint. For simple home or office computer will be enough 2 GB. For home multimedia can be installed from 4 GB of memory. If you have game computer or you often use "heavy" professional programs you can install from 8 GB or more of RAM.
- Clock frequency... The bigger, the better. But here you also need to watch that this frequency is supported by the motherboard and processor. Otherwise, if the RAM frequency is higher than that supported by the motherboard, the RAM will work at lower frequencies, which will mean an overpayment for unnecessary performance for you.
- Timings... This is the delay between accessing memory and until the moment it issues the required data. Accordingly, the lower the delays, the faster the RAM will work.
This is where I will end. I tried to present the basic information on the computer's RAM, which will be enough for an ordinary user to understand what RAM is, what it is for and how it works, its main characteristics. In the comments, you can ask me questions if something is not clear to you.
If your computer becomes slower, additional RAM may be the solution. In this case, you need to figure out what RAM is and what it is for, find out its parameters, and also familiarize yourself with the recommendations for installing and replacing this module.
What is RAM?
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. It is also called:
- RAM (Random Access Memory);
- random access memory;
- or just RAM.
Photo: Random Access Memory
RAM is a volatile computer memory that has random access. During computer operation, it is there that all intermediate, input and output data that the processor processes are stored. All data on RAM can be accessed and saved only when the device is powered. Even with a short-term power outage, information can be distorted or completely destroyed.
Data exchange between Random Access Memory and the processor takes place:
- directly;
- through registers in ALU;
- through the cache.
OP is:

RAM usage
Operating systems for information processing, as well as data storage, which are often used, use random access memory. If modern devices did not have Random Access Memory, then all operations would be much slower, since it would take much longer to read information from a permanent memory source.
Also, multithreading would be impossible. Thanks to the presence of the OP, all applications and programs start and run faster. At the same time, nothing complicates the processing of all the data that is in the queue. Some operating systems, such as Windows 7, have the ability to store files, applications, and other information that the user frequently uses in memory.
Thus, there is no need to waste time while they start to boot from disk, since the process will start immediately.
As a rule, this will cause Random Access Memory to be constantly loaded by more than 50%. This information can be viewed in the task manager. Data has the ability to accumulate and those applications that are used less often will be replaced by more necessary ones.

By far the most common is dynamic random access memory (DRAM). It is used in many devices. At the same time, it is relatively inexpensive, but it works slower than static (SRAM).
SRAM has found its way into controllers and video chips, and is also used in processor memory caches. This memory has a higher speed, but it takes up a lot of space on the die. In turn, manufacturers decided that volume is much more important than accelerated work, so DRAM is used in computer peripherals. In addition, dynamic memory costs an order of magnitude less than static memory. Moreover, it has a high density. This allows more memory cells to fit on exactly the same silicon crystal. The only drawback is its not as fast as SRAM.

It should be borne in mind that all the information contained on the OP can only be accessed when the device is turned on. After the user exits the program, all data will be deleted. Therefore, before exiting the application, you must save any changes or additions that have been made.
OP consists of several cells. This is where all the data is located. With each saved change, the latest information is deleted, and new information is written in its place. The number of cells depends on the size of the Random Access Memory. The larger this volume, the higher the performance of the entire system.
To find out the RAM of your computer, you need to do the following:
- for Windows XP:
- hover the cursor over the shortcut "My Computer";
- then you need to press the right mouse button;
- select "Properties";
- go to the "General" tab;
- for Windows 7:

Install
Additional OP will help to significantly improve the performance of the device. It can be installed both on a stationary computer and in a laptop.
Installing RAM on a computer
First you need to figure out what type of OP is required. Its type depends on the motherboard. In order to find out which type is compatible with the motherboard, you should check the documents for the device or visit the manufacturer's website. When choosing RAM, it is recommended to purchase 2 or 4 modules. Thus, if you need 8 GB of RAM, then it is better to buy 2 x 4 GB or 4 x 2 GB. It is worth paying attention to their bandwidth and speed. All data must be the same. Otherwise, the system will adjust to the lowest settings. This may cause performance degradation.

Photo: RAM installed
To install RAM, follow these guidelines:
- you need to disconnect the monitor, mouse, printer and keyboard from the device;
- make sure there is no static charge;
- remove old modules - for this you need to open the clamps located on both sides and remove the module;
Important! The new OP module should be held so as not to touch the microcircuits that are on the side and bottom contacts.
- The RAM must be inserted in such a way that the groove is exactly aligned with the protrusion located in the slot;
- press the board and fix it, while the clamps should close;
- build a computer;
- turn on the device;
- check for OP.
Installing RAM on a laptop
For this you need:
- correctly determine the type of OP;
- eliminate static charge;
- disconnect the laptop from the power supply and remove the battery;
- remove the desired panel on the bottom of the laptop;
Important! Most laptops do not require paired modules.

Type and volume
At the moment, there are several types of OP. It:
- DDR RAM;
- DDR2 RAM;
- DDR3 RAM.
They differ in the design of the bar, as well as in performance.

Important! It should be noted that the modules are completely incompatible with each other, since they have different connectors for mounting.
Most modern laptops have a DDR2 or DDR3 OP. Legacy models work with DDR. The speed and performance of the computer directly depends on the amount of RAM.
Now there are modules on the market with the volume:
- 512 MB;
- 1 GB;
- 2 GB;
- 4 GB;
- 8 GB.
Before purchasing additional modules, it is worth considering that a 32-bit operating system will only be able to recognize 4 GB. Therefore, there is no need to spend money on boards with a large volume due to the fact that it will not be used anyway. But if the operating system has 64 bits for it, you can install 8, 16 or even 32 gigabytes of memory.
Video: increase RAM
Frequency and other parameters
Among the main parameters of Random Access Memory, the following should be highlighted:

- DDR - 2.2 Volts;
- DDR2 - 1.8 Volts;
- DDR3 - 1.65 Volts.
- module manufacturer. Preference should be given to well-known brands and models that have the greatest number of positive reviews. This will help eliminate the possibility of buying a defective part, and the warranty period will be longer.
What does RAM look like in a computer?
The OP of a computer is a plate consisting of several layers of PCB. It contains:
- printed circuit board;
- soldered memory chips;
- there is also a special connector for connection.

Where is the RAM located? The OP is located directly on the motherboard.

There are slots for modules, usually 2 or 4. They are located next to the processor.

Photo: storage device on the motherboard
OP for PCs and laptops
The RAM intended for a laptop has several differences from the RAM used in a PC, namely:
- modules differ in their size - the plate for a laptop is much shorter than the standard one for a computer;
- the bracket also has unique connectors.

Thus, the module used for the PC cannot be installed in the laptop.
Random access memory is one of the main parts in a computer. She is responsible for the speed of launching various programs and applications, as well as for the temporary storage of information. In addition, it is used to connect external devices and the hard disk with the processor.
- Pythagoras and the Pythagoreans. The doctrine and school of Pythagoras. Philosophy of Pythagoras In the philosophy of Pythagoras, the core was
- Complementarity principle
- The problem of consciousness in the history of philosophy
- Dualism - what is it in psychology, philosophy and religion?
- Topic of lecture subject and history of development of pathopsychology lecturer
- Goddess Demeter: all about her
- Development of ideas about pathopsychology in the pre-revolutionary period

 Live Journal
Live Journal Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter