How to set up a vpn connection on windows 7. How to connect a VPN connection and configure it correctly on Windows

Today, VPN technologies have firmly entered everyday life and are well-known not only by IT specialists, so we decided to update a number of old articles, significantly supplementing and expanding the information they contain. Where ten years ago VPN was mostly reserved for fairly large organizations, today it is widely used everywhere. In this article, we will look at what a VPN is in 2019, what technologies are available, what are their advantages and disadvantages, and how it can all be used.
First of all, let's define the terminology. VPN (Virtual Private Network, virtual private network) is a generalized name for technologies that allow building a logical (virtual) network over a physical one, most often over the Internet or other networks with a low level of trust.
VPNs are commonly used to build networks. tunnels, tunneling is the process of establishing a connection between two points using encapsulation, when the data of one protocol is placed in the "envelopes" of another protocol in order to ensure their passage in an inappropriate environment, ensure integrity and confidentiality, protect with encryption, etc. etc.
Those. if we approach the issue of terminology strictly, then VPN should be understood as a virtual network that is formed by establishing tunnel connections between individual nodes. But in practice, the terms are used much more loosely and very often cause serious confusion. Let's say that the now popular Internet access via VPN is not actually a virtual private network, but is a tunnel connection for accessing the Internet, from a logical point of view, it is no different from PPPoE, which is also a tunnel, but no one calls it a VPN.
According to the organization scheme, two large groups can be distinguished: client-server technologies and just tunnels. In the name of the former, it is usually customary to use the VPN abbreviation, while the latter do not. Tunnels require a dedicated IP address at both ends, do not use ancillary protocols to establish a connection, and may not have link control tools. Client-server solutions, on the contrary, use additional protocols and technologies that establish communication between the client and the server, control and manage the channel, and ensure the integrity and security of transmitted data.
Below we will look at the most popular types of tunnel connections that are used to build VPN networks, starting with classic solutions.
PPTP
PPTP ( Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol, point-to-point tunneling protocol) - one of the most famous client-server protocols, has become widespread due to the fact that, starting with Windows 95, the OSR2 PPTP client was included in the OS. Currently supported by almost the entire range of systems and devices, including routers and smartphones (the client has been removed from the latest versions of macOS and iOS).
Technically, PPTP uses two network connections: a control channel running over TCP and using port 1723 and a GRE tunnel for data transfer. Because of this, there may be difficulties using mobile operators in networks, a problem with the simultaneous operation of several clients due to NAT, and the problem of forwarding a PPTP connection through NAT.
Another significant drawback is the low security of the PPTP protocol, which does not allow building secure virtual networks on it, but its wide distribution and high speed make PPTP popular where security is provided by other methods, or for Internet access.
L2TP
L2TP ( Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) - developed by Cisco and Microsoft, uses a single UDP connection on port 1701 to transmit data and control messages, but does not contain any built-in information security tools. An L2TP client is also built into all modern systems and network devices.
Without encryption, L2TP has been widely used and is used by providers to provide Internet access, thus ensuring the separation of free on-net and expensive Internet traffic. This was true in the era of home networks, but this technology continues to be used by many providers to this day.
To build a VPN, L2TP over IPsec (L2TP / IPsec) is usually used, where IPsec operates in transport mode and encrypts the data of the L2TP packet. In this case, an L2TP tunnel is created inside the IPsec channel, and in order to establish it, it is necessary to first provide an IPsec connection between the nodes. This can cause difficulties when working in networks with traffic filtering (hotel networks, public Wi-Fi, etc.), causes problems with L2TP / IPSec forwarding through NAT and the work of several clients due to NAT at the same time.
The advantages of L2TP include high prevalence and reliability, IPsec does not have serious vulnerabilities and is considered very secure. Minus - high load on the equipment and low speed.
SSTP
SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol, secure socket tunneling protocol) - a secure VPN protocol developed by Microsoft, refers to the so-called SSL VPN, is distributed mainly in the Windows environment, although clients are available in many modern OS environments. There are also third-party server solutions, say in Mikrotik.
Technically, SSTP is a PPP tunnel connection inside an HTTPS session on standard port 443. Only HTTPS headers are available to an outside observer, the presence of a tunnel in traffic remains hidden. This allows you to work successfully in any networks, since HTTPS is widely used to access sites and is usually allowed, it removes the problem of forwarding or operation due to NAT. Safe.
The advantages include integration into the Windows environment, security, the ability to work through NAT and firewalls. The disadvantages are weak or insufficient support from other operating systems and network devices, as well as vulnerability to some classic SSL attacks, such as "man in the middle".
openvpn
OpenVPN is a free and open source VPN implementation. SSL is also used to secure the connection, but unlike SSTP, OpenVPN headers differ from standard HTTPS, which makes it possible to uniquely determine the existence of a tunnel. To transfer data within an SSL channel, OpenVPN uses its own protocol with UDP transport, it is also possible to use TCP as a transport, but this solution is undesirable due to high overhead.
OpenVPN provides high security and is considered one of the most secure protocols, providing an alternative to IPsec. There are also additional features in the form of transferring the necessary settings and routes from the server to the client, which makes it easy to create complex network configurations without additional client configuration.
In addition to tunnels operating at the network layer (L3) - TUN, OpenVPN allows you to create link (L2) layer connections - TAP, allowing you to link networks at the Ethernet level. However, keep in mind that in this case broadcast traffic will be encapsulated in the tunnel, and this can lead to an increased load on the equipment and a decrease in the connection speed.
Despite the fact that OpenVPN requires the installation of additional software, the server part is available for Windows and UNIX-like systems, and the client part is also available for mobile devices. Also, OpenVPN support is available in many router models (often in a limited form).
The disadvantages include work in user space and some complexity of settings. The speed inside OpenVPN tunnels can also be significantly lower than the link speed.
Despite this, OpenVPN is very popular and widely used both in corporate networks and for Internet access.
GRE tunnel
GRE ( Generic Routing Encapsulation, Generic Route Encapsulation) is a tunneling protocol developed by Cisco and is designed to encapsulate any OSI network layer protocols (i.e. not only IP), GRE works directly over IP and does not use ports, does not go through NAT, protocol number 47.
GRE requires white IP addresses on both sides of the tunnel and is a stateless protocol, i.e. does not control the availability of the opposite node in any way, although most modern implementations contain additional mechanisms to determine the state of the link. Also, there are no security mechanisms, but this is not a disadvantage, since, unlike client-server solutions, GRE tunnels are used in corporate and telecommunications environments, where other technologies can be used to ensure security.
To build secure solutions, GRE over IPsec is usually used, when the GRE tunnel is located over a secure IPsec channel, although another solution is possible - IPsec over GRE, when a secure connection is established inside an unencrypted GRE tunnel.
GRE is supported on UNIX-like systems, network equipment (excluding home models), and Windows Server since version 2016. This protocol is widely used in telecommunications and corporate environments.
IP-IP tunnel
IP-IP ( IP over IP) is one of the simplest and least overhead tunneling protocol, but unlike GRE, it encapsulates only IPv4 unicast traffic. It is also a stateless protocol with built-in security mechanisms, usually used in conjunction with IPsec (IP-IP over IPsec). Supported by UNIX-like systems and network equipment. Like GRE does not use ports and does not go through NAT, protocol number 4.
EoIP tunnel
EoIP ( Ethernet over IP) is a link layer (L2) tunneling protocol developed by Mikrotik that works based on the GRE protocol by encapsulating Ethernet frames into GRE packets. Allows you to connect remote networks at the link level (which is equivalent to a direct connection with a patch cord between them) and provide communication without using routing. It should be understood that such a connection involves the passage of broadcast traffic, which can significantly reduce the performance of the tunnel, especially on narrow channels or channels with high delays.
At the same time, EoIP can be useful for connecting commercial and industrial equipment that cannot work at the network (L3) level with routing. For example, to connect remote cameras to a DVR.
Initially, EoIP was supported only by Mikrotik equipment, today its support is implemented in Zyxel equipment and there are packages for its implementation in a Linux environment.
IPsec
IPsec ( IP Security) - a set of protocols for ensuring the security of data transmitted over IP networks. It can also be used not only to protect existing communication channels, but to organize independent tunnels. But IPsec tunnels have not been widely used for a number of reasons: configuration complexity, configuration error criticality (security can be severely affected), and the inability to use routing to control traffic in such tunnels (the decision to process IP packets is made based on IPsec policies).
Conclusion
When rewriting this article, we did not set the task to embrace the immensity; it is impossible to consider all existing VPN solutions within the framework of one article. Its purpose is to acquaint the reader with the main technologies used today for building virtual private networks. At the same time, we deliberately left behind the scenes solutions from Cisco or other "adult" manufacturers, since they are implemented by professionals who clearly do not need such articles.
Also, we did not consider solutions without broad support from network equipment manufacturers, although there are quite interesting products there. For example, the SoftEther VPN multi-protocol server, which supports L2TP, SSTP, OpenVPN and its own SSL VPN protocol, has extensive networking capabilities, a graphical client for configuration and administration, and many other goodies. Or the promising WireGuard, which is characterized by simplicity, high performance and the use of modern cryptography.
However, which technology should be used? It all depends on the scope. If the task is to connect two offices with dedicated IP addresses, then we would recommend using GRE or IP-IP, if the ability to configure remote networks is limited, then you should look towards OpenVPN, it is also suitable if remote networks are behind NAT or do not have dedicated IP.
But to organize remote access, you should use one of the protocols with native support in the systems or devices used by users. If your infrastructure is based on Windows systems and there is no question of access from mobile devices, then you should pay attention to SSTP, otherwise it is better to opt for universal L2TP.
PPTP in today's environment cannot be considered reliable due to weak security, but can remain a good choice if the data in the tunnel will be transmitted using one of the secure protocols. Let's say for HTTPS access to a corporate portal or a web version of a corporate application that also works via SSL. In this case, the VPN will provide additional authentication and narrow the perimeter of the attack on the application; the security of the channel itself will not play a decisive role in this case.
The organization of VPN channels between company branches is of great importance in the work of any IT specialist. This article discusses one of the ways to implement this task based on the OpenVPN software product....We have already talked about port forwarding (forwarding) on a router running Ubuntu Server, however, having considered the general principles, we left private implementations unattended. One of the special cases is the publication of a PPTP VPN server, which causes...
VPN - private virtual computer networks, generalizing the name of a technology that allows you to create virtual networks over other physical networks, for example, a global one. Thanks to the use of a reliable encryption system for information transmitted in such networks, its reliability and security does not depend on the level of security of the underlying web. In VPN, it is possible to use the virtual port of the VPN server, which operates on the basis of the TCP / IP protocol.
The classic scheme allows you to create a virtual connection over the Internet in a point-to-point topology to a server remotely. The latter responds to the request, authenticates it, and sends a response, allowing data to be exchanged between the client and the enterprise's private network. VPN connection gives users the ability to access the network remotely through the Internet channel.
Most providers use VPN technology to provide Internet access services to customers. Today we will consider how such a connection is configured in Windows 7.
Configuration algorithm
Setting up a connection to a remote VPN server begins with the fact that you need to find out the address of the server to which we will connect. You can find it out from your system administrator or provider if you are connected to the Internet using VPN.
- Open the context menu of the network connection icon and select the second item of the drop-down menu, as shown in the screenshot.
- Click on the item where you are setting up a new connection.

- We select the third option from the list of valid connections - to the workplace and click "Next".

- We choose the formation of a new network connection to the Internet from the options offered by Windows 7.

- In the next dialog box, enter the Internet address of the server.
It can be an IP address consisting of numbers, or a domain name of the server that we enter every day to enter various Internet resources. You can get it from the provider that provides Internet access services (by phone, on the official website of the company or in the contract that was concluded during the connection to the network).
Here we also set the name of the connection and, if necessary, allow other users of the Windows computer to use the new connection.

- Next, enter the username that was assigned to you to authorize and connect to the remote server, and the password for the account.

- Click "Connect".

Within a few seconds, a request will be sent to the specified server, and when authorized, the Windows 7 computer will be able to connect to the specified source.
- Close the window or click "Connect Now" to immediately make a new connection.

The creation of a VPN is over, there remains a fine-tuning of the connection for the convenience of its use.
- We visit the control panel item responsible for managing network connections, where we click "Connect to the network".

If the connection has not been established, then you will have to go to "Change adapter settings", call the context menu of the connection created in Windows 7 and select "Connect".

It's no secret that many people, in some cases, use a virtual private network, or VPN, when connecting to the internet on their computer or smartphone. It may seem paranoid, but there are real threats and situations are only getting worse. On Wi-Fi networks, unscrupulous people may try to intercept your information. And whenever you connect to the internet, your Internet Service Provider (ISP) has access to everything you send. On the web, advertisers and spies can track your movements between websites and distinguish your location by looking at your IP address. This is scary! And in order to prevent and protect yourself, you need to use a VPN, and we will describe how to set up a VPN in this article.
The fact is that the internet itself was not designed to protect your privacy. It was created for easy information sharing, not user privacy, anonymity, or encrypted communications. Although the HTTPS protocol is designed to protect your information, it does not protect against Internet attack attempts or local network attacks, which is a serious problem if you have ever used a connection that does not belong to you. For example, in a hotel or cafe.
So a more private, closed internet won't become a reality (perhaps never), using a VPN is the easiest way to make sure you're sharing as little information as possible.
What a VPN Does and Doesn't Do
As with any security tool, it's important to understand the capabilities of a VPN.
After all, you don't expect a Kevlar vest to save you from falling out of an airplane, it's designed to stop a bullet.
When you turn on the VPN, your traffic is routed through an encrypted tunnel to a server operated by the VPN company. This means that your ISP or anyone connected to your router will not be able to see your web traffic. From the VPN server, your traffic goes to the Internet.
Because your traffic is coming from the VPN server, your actual IP address is hidden. This is important because IP addresses are distributed geographically and can be used to determine location. If someone checks your IP address, they will see the IP address of the VPN server. This can come in handy if you want to fake your location. By connecting to a VPN server in London, it looks like you are connecting to the internet from the UK.

What a VPN won't do is completely anonymous traffic. To do this, you will need to use Tor. This excellent anonymization is easily accessible through a special version of the Firefox browser. Instead of just sending your data through one VPN server on the network, your data is sent through several different computers. This makes it much harder for those who are trying to track your activities and understand what you are doing.
In addition, websites can track your movements using cookies, online trackers, and other sophisticated tools. Using an ad blocker like Adblock Plus helps keep these nasty things down and makes it a lot harder to access and make it harder for advertisers to learn your movements on the web.
Finally, just because you have a VPN doesn't mean you can forget the basics of security. While some VPN services claim that they can block malware, we recommend standalone antivirus software for your computer because these tools are designed specifically to protect your computer from malware. Another precaution is to use common sense when clicking on links or opening email attachments. Phishing attacks - where an attacker uses a dummy website that mimics someone you know to trick you into entering your credentials - are very common, so stay on the lookout.
How to choose a VPN
When we consider a VPN, there are several key metrics we look for. First, the VPN service must allow you to connect to at least five devices at the same time. Another is whether the VPN service supports BitTorrent traffic on its servers.
Speaking of fees, the average cost of a VPN service is $10.53 per month. A VPN service that charges more per month has to offer something substantial, like a great interface or plenty of server locations to sweeten it up. You can usually get a discount if you're buying long term, but we recommend avoiding them until you're sure you're happy with the service.
Before signing up for a VPN, be sure to read its terms of service.
This document will outline the information the VPN collects and what it does with that information. Most companies say they don't log traffic, which is great. Others go further by saying that they don't monitor user activity at all. This is important because the VPN provider has access to all the information you are trying to protect from others. Be sure to read this question and consider trying a different service if the terms don't work for you. The most important thing about a VPN is trust. If the location, pricing, or terms of service don't fill you with confidence, try a different service.
Free VPN or Paid VPN?
Recently, we at WoW IT conducted a survey of 1,000 people asking questions about VPN usage.
According to our results:
- 62.9 percent said they didn't want to pay more than $5 per use.
- 47.1 percent said they want to use a free VPN.
Some services offer a free trial, but usually for a limited time. Others, such as TunnelBear and AnchorFree Hotspot Shield Elite, have completely free versions but may limit some features for paid users. For example, TunnelBear has a data surcharge for free users. On the other hand, Hotspot Shield has a free, ad-supported version. The Opera browser, until recently, had a free VPN and didn't charge anything for using it. Opera separately offers excellent VPN apps for Android and iOS, also completely free, extending your protection wherever you are.
How to set up a VPN and get started with it
After you buy a service, the first thing to do is download the company's app. The VPN service website usually has a download page. Next, download applications for your mobile devices; you'll want to secure as many of your devices as possible. Typically, you pay one subscription fee for a certain number of licenses (usually five), you can use this service on any device for which applications are provided. If suddenly you have problems and you can’t set up a VPN, the support service of the company where you purchased the VPN will always come to your aid. This is another plus of a paid application. 
Once you've installed the app, you'll be prompted to enter your login details. In most cases, this is the username and password you created when you signed up. Some companies, such as Private Internet Access, assign you a username that is different from your login credentials to give customers more privacy.
After logging in, your VPN app will usually connect to the VPN server closest to your current location. This is to ensure faster speeds with a VPN, as latency and speed reduction increase with the distance to the VPN server from your actual location. Like this: Your information is now securely tunneled to the VPN server.
Note that you don't have to install the VPN company's app. Instead, you can configure your device's network settings to connect directly to the VPN service. If you're concerned about in-app surveillance, this might be a good option for you. Most VPN services will have documentation on how to set up your device.
Perhaps you want to spoof your location, use BitTorrent over a VPN, or want to take advantage of some of the custom servers provided by your VPN company.
 Many VPN companies include an interactive map as part of their app. For example, NordVPN allows you to click on countries to connect to these servers. This is a useful way to understand where your information is going.
Many VPN companies include an interactive map as part of their app. For example, NordVPN allows you to click on countries to connect to these servers. This is a useful way to understand where your information is going.
The choice of server depends entirely on what you want to achieve. For security and speed, you should choose a server that is nearby. To access region-specific content, you need a server that is local to the content you want to watch. If you're trying to watch the BBC, you need to sneak into the UK. Some VPN companies, such as KeepSolid VPN Unlimited and NordVPN, have dedicated video streaming servers.
These dedicated servers are useful because streaming services like Netflix block VPNs. It's about licensing Netflix deals. For example, Netflix has the right to provide Star Trek: Discovery outside the US, but in the US you need to pay for the service.
It's also a good idea to check if your VPN service is giving BitTorrent traffic on any server or only certain ones. NordVPN clearly states that the servers do not provide torrent traffic.
Other services like NordVPN and ProtonVPN have advanced security options like access to Tor or multihop virtual networks. Tor, as mentioned above, is a way to better protect your privacy and allows you to open hidden websites on the so-called Dark Web. Multihop VPN instead of just routing your traffic through one VPN server, connecting through multiple hosts connects you to one server and then to another.
If you choose to ignore third-party apps and manually configure your network settings, you may need to enter information for each VPN server separately.
Advanced VPN settings
The feature set in each VPN varies from service to service, so we can only generalize what you can see when you open the Settings panel. But we recommend that you read the documentation and try clicking a few buttons. After all, the best way to learn how to use a tool is to try it out.
Most VPN services include a Kill-Switch feature. Once enabled, this setting prevents the computer from sending or receiving information over the Internet unless a VPN is enabled. This is useful when your computer disconnects from the VPN and it can prevent small pieces of data from getting through to unencrypted ones.
We recommend using the OpenVPN protocol. Open source, so as many potential vulnerabilities have been tested and you can set up a VPN with ease. IKEv2 is also a good, secure option if OpenVPN is not available. Please note that on some platforms, such as macOS and iPhone, OpenVPN is not always available due to additional restrictions set by the developers. The best VPNs for iPhone give you access to the latest and greatest protocols available on this platform.
How to set up a VPN and use it?
For maximum security, you should use a VPN as often as possible, and ideally, all the time. But this is an ideal, and it is not always achievable. At a minimum, you should use a VPN when you're using a network that you don't control, and especially if it's a public Wi-Fi network. But in general, we recommend that users set VPN as the default in their apps. You can always disconnect if that causes a problem.
VPNs for Android and other mobile devices are a bit tricky, especially if you move around a lot and get cell phone coverage. Every time you lose and reconnect, the VPN should reconnect. But at the same time, it is less likely that your mobile traffic can be intercepted, but as the researchers prove, this can be done. And given that law enforcement and intelligence agencies have virtually unhindered access to telecommunications data, it is recommended to use a VPN even over cellular. In addition, most mobile devices can automatically connect to any familiar Wi-Fi network. At a minimum, you should be using a VPN when connected via Wi-Fi.
If you're concerned that a VPN is slowing down your connections or blocking important traffic, you should take a look at split tunneling options. Again, different companies give this feature different names, but the bottom line is that you can decide which apps will use the VPN for their traffic and which apps can work without a VPN. For example, TunnelBear includes the option to not tunnel Apple apps to ensure they function properly on a Mac.
How to Set Up a VPN for Streaming with Chromecast or AirPlay
Chromecast and AirPlay let you stream music and videos from your computer or mobile device to speakers, TVs, and streaming boxes. But they all require Wi-Fi, which can be a problem when using a VPN.
When a VPN is enabled, your traffic travels through an encrypted tunnel, preventing devices from finding each other on the same Wi-Fi network. This is as it should be, since you don't want anyone snooping around the network and knowing what you're doing. Unfortunately, this also means that Chromecast and AirPlay won't work if you activate the VPN.
Chromecast Ultra
The simplest solution is to disable your VPN, but that's not the only option. You can use split tunneling as mentioned above to route only the traffic you want to secure through the VPN. You can use a VPN browser plugin that only encrypts your browser traffic and nothing else.
In addition, you can install and configure a VPN on your router. This means that all devices connected to your router, from your phone to your smart juicer, will have encrypted traffic. This is a great option for a smart home.
VPNs are not a rocket
Too many of you don't use a VPN just because they think it's a covert security tool. But many companies have worked hard to make them convenient and easy to use. Most install and forget about security tools, as they should. And while opening your wallet to protect yourself from potential threats is always annoying, buying a VPN is one of the best and easiest ways to protect your web traffic.
If you are unable to set up a VPN or you have problems with it, the WoW IT team is always ready to help.
Good afternoon everyone! Today we will talk about how to set up VPN (Virtual Private Network) in Windows XP, Windows Vista or Windows 7 and Lynix.
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network, which means "Virtual Private Network". VPN is created on top of an existing network, such as a regular local area network or the Internet, and can connect computers in different parts of the world into one logical network. In this case, all data transmitted over such a network is usually encrypted to protect against unauthorized listening and interception. Thus, traffic encryption is one of the main advantages of using virtual private network technology. If computers are physically connected to each other by cable or radio waves (wi-fi), then their logical connection via VPN is possible only using special equipment called a VPN server. It may just be a computer with special software. The VPN server manages the connection of other (regular) computers to the virtual network.
A special VPN connection is configured on a computer connected to a virtual private network, in the configuration of which the name of the VPN server and other parameters necessary for a successful connection are specified. In each case, these parameters may vary, but the sequence of actions when creating a VPN connection is the same. We will consider it using the example of Windows Vista and Windows XP operating systems.
Setting up a VPN connection in Windows XP
This section describes how to set up a VPN in Windows XP.
New Connection Wizard
Push button "Start" in the lower left corner of the desktop, in the main menu of the system that appears, select the item "Control Panel" if your control panel looks like "XP Style" and you can't find the icon "Network connections", switch to the classic view of the panel by selecting the appropriate item on the left side of the window:
or select "Network connections" straight from the main menu "Start":

If you have a classic view window, find the icon in it "Network connections" and open it, in the window that opens, find and run "New Connection Wizard":

In the first window, just click the button "Further":

In the second, choose "Connect to the network at the workplace" and press the button "Further":

In the third select "Connecting to a virtual private network" and press the button "Further":

In the fourth field, enter a name for your connection in the free field, for example, Internet VPN and press the button "Further":

On some computers with other connections, between step 4 and step 5, an additional window appears asking you to dial a number to connect. In this case, you must refuse to dial the number and go to step 5.
In the fifth window, enter the IP address of the main access gateway nas.iksnet(or nas3.iksnet for some subscribers) and click the "Next" button (note that there should not be any spaces or other invisible characters before and after the server name):

In the sixth, for convenience, check the box "Add connection shortcut to desktop" and press the button "Ready":

Connection Properties
After that, you will immediately open the connection window, at the bottom of the window, find the button "Properties" and click on it:

Or click the button "Cancel" and with the connection selected, right-click on it and select "Properties":

In the window that opens, select the tab "Parameters", uncheck the box "Enable Windows Logon Domain":
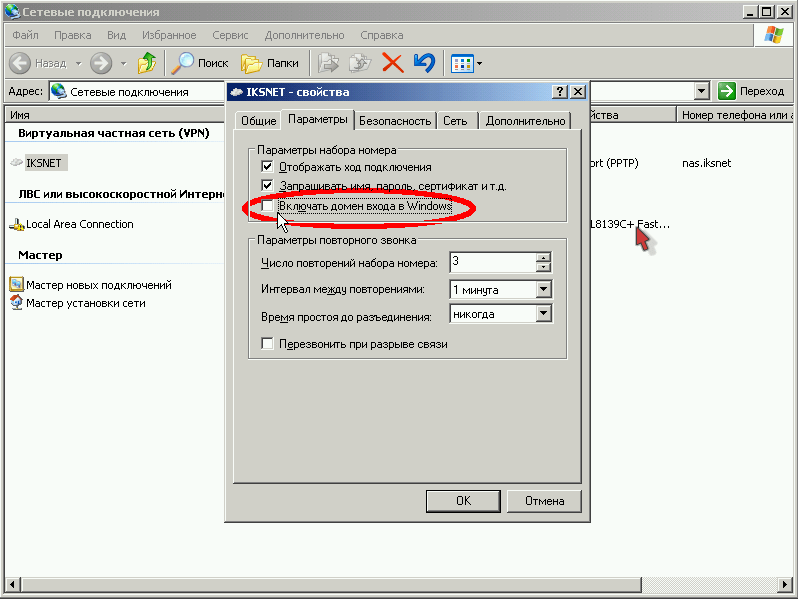
In the "Security" tab, take off tick off the item "Data Encryption Required" and click on the "OK" button:

On the tab "Parameters" you can check the box next to "Call back when disconnected", then, in case of an unexpected break, the connection will be restored on its own:


Connecting:

Now in the field "User" you need to enter your contract number ( for those subscribers who have a three-digit contract number, add “0” in front! For example, an agreement 111 typed as 0111 .), and in the field "Password", your access password to view statistics and mail from the contract. Please note that there should not be any extra spaces after the contract number in the "User" field.

After a successful connection, for ease of use, on the tab "Parameters" you can uncheck "Request name, password, certificate, etc.", after that the username and password will no longer be requested.
Password saving
Attention: saving the password in the system is not recommended, because the saved login and password can be stolen by spyware or your computer can be used to access the Internet in your absence.
Please note that access to the Internet is controlled by name and password, so take this moment more seriously. Do not disclose this data to strangers. If your password is too simple and short, in order to increase security, we suggest changing it. You can do it yourself, from your workplace, using the client part of the new settlement system, available at the link: Statistics. There you can change the password separately for entering the statistics page and separately for accessing the Internet. We hope that there you can still find a lot of new, interesting and useful!
Note
When the VPN connection is disabled, you can freely use the resources of the local network, just as before, a VPN connection is only needed to access the external network. If you turned off, then to create a VPN connection, be sure to turn on "LAN connection" otherwise, the VPN connection will fail.
Mistakes
Most often, the system produces the following errors:

Error 619 or 734
- Occurs if you forgot to uncheck the "Required data encryption» in the connection properties tab «Security».
Error 629
This error occurs if your username and password are already connected (remember if you let someone you know use your Internet), if not, then this connection is not broken on the server. To do this, wait 10 minutes, and try to connect again after this time ... If nothing helped on the 3rd attempt, then I advise you to contact support.
Error 650
"The remote access server is not responding":
- The Internet access server is unavailable. Check if “Local Area Connection” is enabled, if the network card is working, if the network cable is working, if a specific IP address is set in the IP connection settings.
Error 651 or 800
Your modem (or other device) reported an error" or "Unable to connect to VPN connection server"
- These errors may occur if you deleted or disabled the old "Local Area Connection" connection.
- Or if you specified in step 5 wrong address. Check it out, make sure the numbers are separated by dots and not commas.
- Firewall blocks outgoing requests for VPN connections.
- For some reason, the request does not reach the server, i.e. perhaps the gateway of your segment does not allow the request due to the load or failure.
- The server sends a response about the inability to connect. There are currently a large number of concurrent connection attempts.
Possible Fixes
- Check if the local network is working at this point in time.
- Check the passage of the signal with the ping command to your gateway, and then to your authorization server.
- Fix a pair of keys in the registry or reinstall Windows
Error 678
"No response received"
- If it doesn't help, then try re-creating the VPN connection again (pay attention to the connection type, it should be PPTP, not PPPoE or L2TP).
- Also, this error can occur when negative balance your personal account.
Error 679
- This error occurs when the network adapter is disabled. You need to enable the network adapter by going to "START->Control Panel->System->Device Manager->Hardware".
Error 691 or 718
"Wrong login or password"
- Check if the login (contract number) is entered correctly. It must be 4-digit (three-digit contract numbers must be padded with a zero in front). Try typing your username and password again. When typing, check that the correct keyboard layout (setting language) is enabled, the status of the Caps Lock indicator.
- Or if at the moment
- If the operating system does not prompt you to enter a username and password when connecting, then you must perform the following steps: Open the "Control Panel", select "Network Connections", right-click on your VPN connection and select "Properties" from the menu. The VPN connection properties will open. Now you need to go to the "Settings" tab and check the box next to "Request a name, password, certificate, etc." After that, confirm the changes by clicking the "OK" button. The next time you connect, you will be prompted for a username and password.
Error 711
This error occurs if a required service is not running on the computer. In this case, it is impossible to connect to the network, and in some cases - installation of network adapters. This issue may occur if some or all of the following services are not running.
- Plug and Play plug and play support
- Remote Access Automatic Connection Manager
- Remote Access Connection Manager
- Telephony
To resolve this error, follow these steps for each of the above services.
- Open Administrative Tools by clicking the Start button and selecting Control Panel, System and Maintenance, and Administrative Tools. Administrator Permission Required Enter an administrator password or password confirmation if prompted.
- Double click Services. Administrator Permission Required Enter the administrator password or confirm the password if prompted.
- Right-click one of the above services and then click Properties.
- On the General tab, under Startup Type, select Manual.
- Click Apply and then click Run.
Error 720
"Unable to connect to remote computer."
This error occurs when the network protocol stack in Windows is corrupted. You can check the integrity of the stack using the netdiag utility.
- Enter command
- The Netdiag tool will display the results of checking a number of network components, including Winsock. For more information about this check, type the netdiag command in the following form:
- If the Netdiag tool reports an error, you must restore the Winsock2 registry key.
- The easiest and fastest way to solve:
- After that, we restart the computer and set up a local network connection, since executing this command overwrites the registry settings that are used by the TCP / IP protocol stack, which is tantamount to deleting and reinstalling it. Re-create the VPN connection if necessary.
- If this does not help, then you can completely reinstall the TCP / IP stack like this:
- Delete the registry key with the command REG DELETE HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Winsock
- Delete the registry key with the command REG DELETE HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Winsock2
- Restart your computer
- Open the %winroot%\inf folder
- Find the file nettcpip.inf in it, make a backup copy of it and then open it in a text editor (for example, Notepad).
- Find the lines in it:
- Fix them to:
- Save changes to nettcpip.inf file
- Open Network Connections and by right-clicking on the property of the network connection we need, select Install-> Protocol-> Add. Next, select "have disk" and specify the path %winroot%\inf (usually this folder is hidden!)
- Select TCP/IP from the list. After that, you will again be taken to the network connection properties window, but for TCP / IP, the Uninstall button will now be active.
- Select TCP/IP from the This connection uses the following items list and click the Uninstall button.
- Restart your computer
- Set the TCP/IP protocol in the same way as steps 2-5.
- If all of the above does not work, then see the instructions at
Error 733
- Occurs if you forgot to uncheck all protocols except Internet protocol and QoS.
Error 734
- You most likely have a virus WIN32.Sality.
Error 735
- "The requested address was rejected by the server": Occurs if you have entered IP address in "TCP/IP Properties"(it should come automatically).
Errors 741 - 743
"Encryption settings are incorrectly configured"
- Go to the VPN connection settings, and in the "Security" tab, disable the "data encryption" item.
Error 764
"Smart card readers are not installed"
- This error occurs if you configured the VPN connection incorrectly. Try to remove it and set it up again according to this instruction.
Error 769
"The specified destination is unreachable"
- The error occurs due to a disabled LAN connection or lack of a physical link. It is recommended to check the status of the LAN (should be enabled) and the physical connection to the network (network cable must be connected).
- Sometimes it occurs if the router for some reason did not issue the correct IP address via DHCP
Error 781
"The encoding attempt failed because no valid certificates were found."
- Causes: The VPN client is trying to use the L2TP/IPSec protocol to connect.
- Tip: Enter VPN connection settings-Properties->Network->VPN type and select PPTP VPN
Error 789
"Invalid VPN connection type selected"
- Go to the VPN connection settings and on the "Network" tab, from the "Type of VPN" list, select "Automatic" or "PPTP". Try reconnecting.
- Also, this error occurs if you made a mistake when entering the IP address, and enter commas instead of dots to separate octets.
Error 807
If you are using the "Automatic" type of VPN connection, then try changing it to "PPTP". In the properties of the network card, you need to set Receive-Side Scaling State - disable and Receive Window Auto-Tuning Level - disable. It is also possible that the connection to the access server is being blocked by a firewall. You can also recreate the VPN connection according to the instructions, if the problem is not solved, remove the KB958869 system update, or restore the system to an earlier state.
Error 809
Occurs when:
1 Using the L2TP VPN connection type in Windows Vista and Windows 7 due to Windows Firewall blocking the connection. Solution: Change VPN connection type to PPPtP. Activate the "Routing and Remote Access (PPPtP)" firewall rule
2 Blocked by your installed firewall or antivirus with firewall function Solution: Set up your firewall correctly.
Error 1717
"Unknown interface"
- Try restarting your computer
- If it does not help, then run from the command line (checking the integrity of system files)
Setting up a VPN connection in Windows Vista/7
New Connection Wizard
Similar to setting up a VPN connection in Windows XP, run "Set up a connection or network" and select "Connect via VPN":

Choose to create a new connection and type PPTP, then press the button Further:
If you have not yet created a single VPN connection, then in the window that appears, select "Use my Internet connection (VPN)"
If connections have already been created in the system, then in the window that appears, select "No, create a new connection"

Fill in the field for the server address, check the box Do not connect now and press the button Further:

Enter in the field Username contract number, and in the field Password- the password for the VPN connection (specified in Appendix No. 2 to the contract as the Password for viewing statistics, mail and VPN connection) and press the button Create:

VPN connection properties
After that, select "Properties of the VPN connection" and fix it in the marked places:


If you uncheck "Request name, password, certificate, etc." then when connecting, the computer will not display the connection window and ask for a login and password. If Windows forgets the login and password (and this happens), then the connection will not be established. Error 691 will be displayed. In this case, the user will not be prompted to re-enter the login and password. What to do in this case.



The connection shortcut on the desktop in Windows Vista and 7 can be done as follows: Open the "Network and Sharing Center", in the left column click the link "Change adapter settings", in the window that opens you need to find your "VPN connection" (the name may be different, depending on how you specified the "Destination Name" during setup). Right-click on the connection and select "create shortcut". By default, you will be prompted to place this shortcut on the desktop. We press "Yes".
Mistakes
Error 609
This method of solving the problem does not always work.
- Run Command Prompt (CMD) as Administrator
- Enter the following commands (remove miniport drivers):
- Now the next two (installing the miniport drivers):
Error 619
"Port disabled"
Possible causes and solutions:
- Operating system problems. In this case, we recommend contacting a specialist.
- The firewall (firewall) is enabled. In this case, we recommend disabling the firewall.
Error 651
"Your modem (or other device) has reported an error."
Possible causes and solutions (in order of execution):
- Operating system failure. In this case, we recommend that you restart your computer.
- Broken network card drivers. We recommend reinstalling the drivers and reconfiguring the network.
- OS malfunctions. We recommend reinstalling the operating system.
- The network card is faulty. We recommend replacing the network card.
Error 678
"No response"
Often occurs when the MAC-IP binding is broken. This does not ping the VPN servers and the gateway. In this case, it is recommended to call us and reset the MAC-IP binding.
An error may appear if an attempt is made to connect to a server that does not support the PPTP VPN protocol. We recommend reconfiguring the VPN connection using the autoconfigurator or checking the settings manually.
Error 691 (Vista/7)
"Access denied because the username and password are invalid on this domain."
Appears in the following cases:
- Invalid username/password entered. Completely clear the login / password entry window and type them again. Login must be 4-digit (three-digit contract numbers must be padded with a zero in front). When typing, check that the correct keyboard layout (setting language) is enabled, the status of the Caps Lock indicator.
- The VPN session ended incorrectly (connection failure, abnormal shutdown of the computer). In this case, you need to wait a few minutes.
- Or if at the moment a connection has already been created with your username and password. (If you have more than one computer connected).
- Quite often it happens that Windows “forgets” the entered login and password, and then they must be entered again, having previously erased from the input fields.
- If the operating system does not prompt you to enter a username and password when connecting, then you must perform the following steps: Open the "Control Panel", select "Network and Sharing Center", in the left column click on the link "Change adapter settings", right-click click on your VPN connection and select "Properties" from the menu. The VPN connection properties will open. Now you need to go to the "Settings" tab and check the box next to "Request a name, password, certificate, etc." After that, confirm the changes by clicking the "OK" button. The next time you connect, you will be prompted for a username and password.
Error 711
run in a command prompt with Administrator rights:
Secedit /configure /cfg %windir%\inf\defltbase.inf /db defltbase.sdb /verbose
in order to run the command line with administrator rights, you must click the start menu, then in the run tab, type cmd in the English layout, an icon with the inscription cmd will appear in the menu, right-click on it and select "Run with administrator rights"
Error 814
"No basic ethernet connection found"
- The error is caused by the unavailability of the network adapter used for this connection.
Error 868
"DNS name not allowed"
- This error only occurs on Windows 7. The essence of the problem is that in some "assemblies" (builds) of this Windows, the DNS client is unstable.
- Solution:
- Check that the DNS server addresses in the LAN connection are obtained automatically (currently 10.0.1.5 and 192.168.2.1 should be given)
- Disable the IPv6 protocol (or better, everything except IPv4) in the properties of the LAN connection
- Set access server address instead nas.iksnet as an IP address (10.0.1.11 or 10.0.1.13 at the moment, but it’s better to check with the command
- In some cases, resetting directories helps: at the command line, enter the commands
Setting up a VPN on Linux
Debian
First, install the desired package:
$ apt-get install pptp-linux
Then edit the file with the description of network interfaces. Here is an example:
$ cat /etc/network/interfaces auto lo iface lo inet loopback auto eth0 ppp9 iface eth0 inet dhcp iface ppp9 inet ppp provider iksnet pre-up ip link set eth0 up
Then edit the file describing your VPN connection. It should be something like this:
$ cat /etc/ppp/peers/iksnet unit 9 lock noauth nobsdcomp nodeflate #mtu 1300 persist maxfail 3 lcp-echo-interval 60 lcp-echo-failure 4 pty "pptp nas.iksnet --nolaunchpppd --loglevel 0" name
Then enter your credentials
$ cat /etc/ppp/chap-secrets And after that, you can manually connect the VPN: $ ifup ppp9 And turn off: $ ifdown ppp9 The connection can be checked with the command: $ ifconfig ppp9 ppp9 Link encap:Point-to-Point Protocol inet addr:89.113.252.65 PtP:10.0.1.11 Mask:255.255.255.255 UP POINTOPOINT RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1450 Metric:1 RX packets:40 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:418 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:3 RX bytes:7750 (7.5 KiB) TX bytes:1189 (1.1 KiB) Original article http://www.iksnet.ru/wiki/index.php/%D0%9D%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B9%D0%BA %D0%B0_%D0%BF%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%BA%D0%BB%D1%8E%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%8F_%D0 %BF%D0%BE_VPN Greetings! And straight to the point. What is a VPN server for? It is mainly used to change the IP address and your country in order to bypass various site blocking at work and at home. In addition, a VPN connection helps to encrypt traffic and thus ensures the security of transmitted data. For example, using public Wi-Fi, all data that is transmitted through the network can be "hijacked". Theoretically, these can be any files, but usually they steal passwords from wallets, mail, Skype, and anything else. In this article, we will set up our own VPN server, it is not difficult. Despite the volume of the text, the main action takes up a small part, and the rest is goodies 🙂 The article also has a video. There are a bunch and a small one on the Internet, from free to very paid ones. Disadvantages of free VPN services: Paid Disadvantages: There are also advantages of VPN services - this is ease of use, relative cheapness. So, if you need a specific country or city, or you need a lot of traffic that VPN services do not provide, a guarantee of security, then it makes sense to get confused by setting up a personal VPN server. As a rule, this requires deep knowledge of server system administration. But I tried to explain everything simply so that even the kettle can understand) This method also has disadvantages: Read to the end and I will show you how to use your VPS server to bypass blocking without setting up a VPN on it. There are countless hosting providers on the Internet. All of them allow you to host your websites with them. The most popular service is shared hosting. More advanced is a dedicated virtual server - VPS (VDS is, consider, the same thing). You can host websites on a VPS, raise a VPN server, a mail server, a game server - whatever! You need to know that there are several types of VPS servers: OpenVZ, Xen and KVM. For the VPN server to work, you need KVM. The server type is specified in the hosting tariffs. OpenVZ and Xen are also sometimes suitable, but you need to write to the hosting technical support and ask if the “TUN” module is connected. Without going into details what it is for, just asking. If not, can they turn it on. It doesn't hurt to also ask if VPN as such will work (even on KVM), as some companies cover up this possibility. Oh yes, the server operating system is Debian, Ubuntu or CentOS (generally Linux-like). Server power doesn't matter.
I have a KVM VPS server at my disposal. Here everything works right away, you don’t need to write anywhere. "Hostname" enter any or the name of your site (if you will in the future). "OS Template" select "Ubuntu 14.04 64bit" or any of Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS: The operating system can then be changed, if suddenly something does not work out. After payment, you receive the login details for the control panel and the Root password for setting up the server by mail. And also the IP address of the server, and it will be your IP address when we raise the VPN and connect to it from the computer Press the "Manage" button and get into the administration window: We don't need to touch anything here. The only thing that may be needed is to reinstall the operating system - the “Reinstall” button, more on that later. Now we need to connect to the server in order to send commands to it. To do this, we will use the free Putty program. Unpack the archive with the program and run the file putty.org.ru\PuTTY PORTABLE\ PuTTY_portable.exe In the "Host name" field, paste the IP address of the server that came in the letter, you can also copy it from the control panel: and click "Connect". If such a window pops up, then click "Yes": A black console window (command line) should appear in front of us. This is where we will give commands. But first you need to log in. To do this, in the "login" field, enter "root" Then we copy the root password from the letter and paste it into the “password” field. To paste here from the clipboard, you just need to right-click once on the console window. At the same time, the password is not printed on the screen, it feels like nothing happened. Everything is fine, press "Enter". Lines with information about the system should slip. If you wrote some kind of error, then check everything again. Also, the console will not wait long while you are looking for the root password. If by that time an error pops up, then start Putty again. We are already at the finish line in setting up our own VPN server. There are many instructions on the Internet on how to install a server, but they all require the knowledge of a system administrator, because small nuances are overlooked. To the delight of all dummies, there is a universal “OpenVPN road warrior” script that will do all the work itself. We only need to give the command to download and run it. So, copy this line and paste it into the console window with the right button and press "Enter": wget https://git.io/vpn -O openvpn-install.sh && bash openvpn-install.sh All sorts of lines will skip and, if the script has successfully downloaded and launched, the dialog of the VPN server setup wizard will begin with us: The script finds the expected value for each parameter and offers to agree with it, i.e. press "Enter", or enter your own value. In general, the creation of a VPN server is over, it's time to reap the rewards. During the installation process, the script created a configuration file for our computer. In order for us to use the server, this file needs to be downloaded. To do this, paste into the command line: cat ~/client.ovpn The contents of the "client.ovpn" file will be displayed on the screen. Now it must be carefully copied to the clipboard. Scroll up to enter the command, select all the lines with the mouse, except for the very last one (for new commands), i.e. the last highlighted line will be “
". To copy the selection to the clipboard, press "Ctrl-V". Now, on a computer in Windows 7/8/10, open notepad and paste the copied text into it. We save the file on the desktop under the name "client.ovpn". If you plan to give access to the server to other people, then it is better to create separate files for them, for example vasya.ovpn. To do this, simply run the script again and now select the 1st item - create a new user. Congratulations, we are at the finish line! Now it only remains to install a free program that will connect to our VPN server. It's called OpenVPN. Download the version for Windows and install it, you do not need to run it. If any windows pop up during the installation process, we agree with everything. To connect to the server, right-click on the “client.ovpn” file on the desktop and select “Start OpenVPN on this config file”: A black window will appear with the connection initialization process. If everything went well, then the last line should be something like: A window may also pop up with a question about the type of new network, then select "Public network". You can check, go to the site 2ip.ru and look at your IP, it must match the IP of the VPS server: The server console window can now be safely closed. And in order to close the VPN connection and return the old IP, you need to close the window from OpenVPN. To connect next time, simply right-click the "client.ovpn" file from the desktop, nothing else is required. With phone it’s even easier, you need to install the OpenVPN application through the playmarket, upload the client.ovpn file to memory, select it in the application and connect to our vpn server. If you feel that everything is going wrong because of your mistake, then you can reinstall the operating system on the hosting. To do this, click "Reinstall" in the control panel (see the screenshot of the panel) and select a new operating system (or the same one): Press the "Reinstall" button and wait 10 minutes. A new Root password will also be issued, don't lose it! Most problems occur at the stage of connecting to the server in the OpenVPN program, especially in Windows 8/10. There may be errors in the black window, for example: In this case, the first thing to do is to give the program administrator rights and, accordingly, log into the system with administrator rights. Let's go to "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\bin\", right-click on the openvpn.exe file -> properties. On the Compatibility tab, check the "Run this program as an administrator" checkbox. Now everything should work. More treatment options: You can understand whether the problem is in a computer or laptop if you install the OpenVPN application on your phone or tablet through the playmarket, upload the client.ovpn file to it and connect to our vpn server. If this does not work out, then you need to look for the cause on the server, write to the support service. Pay attention to the messages in the black window, if there are any repeated lines "read from TUN / TAP ... (code = 234)" as well as a message somewhere in the middle "WARNING: 'tun-mtu' is used inconsistently, local...": In this case, open the client.ovpn file in notepad and write in the new very first line: tun-mtu ‘server value’ server value is the number at the end of the line in the text "remote='tun-mtu 1500'". Submit your value! As a result, it should look like this: This is done because for some reason the MTU values on the computer and on the VPS server are different. We leave the .ovpn file for the smartphone untouched! You can use our VPS/VDS server as Proxy Server. To do this, we do everything as before until the moment you click the "Connect" button in the Putty program. No need to open the console and run the script. We go to the tab "SSH-> Tunnel", we prescribe Source Port: 3128 Oops, I finished writing the article later, here I have Putty in English, but the essence is the same. If it says "You need to specify a destination address in the form host.name:port" error, then switch to "Dynamic" instead of "Local". On the "Connection" tab, in the "Seconds between keepalives ..." field, set 100 seconds, this is necessary so that the connection does not break due to downtime. Now we are connected - we press "Open", we enter the login/password. Next, go to the network settings in the browser and set the proxy server there. In chrome it is "Settings->Search settings->write 'proxy'->Proxy settings". We do everything as in the screenshot: Now all sites will work through our server, but only in the browser and some programs. Other programs will not see the proxy, they will work directly. It is necessary in each program in the connection settings, if any, to register the address, port and proxy type: Socks4/5. Or install OpenVPN and don't use a proxy. Install an extension for Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox called . In the settings you need to add our proxy server: On the "URL Patterns" tab, add masks of sites that should be opened through our server. The site mask is its name with asterisks on the sides. That's it, now the added site will go through a proxy, and all the rest will go directly. If you click on the extension icon, you can choose to let all sites through it or none at all. You can connect Putty to a proxy with one click. To do this, before connecting, in the “Connection-> Data” section, register the server login, the one that is usually root Now you need to create a shortcut on the desktop, in which you specify the following parameters: "C:\Program Files\PuTTY\putty.exe" -load myvpn -pw server_password where myvpn is the name of the saved session. Everything, one detail remains - to remove the Putty window from the taskbar to the system tray. You need to download a modification of the utility and replace the exe file. Now in the settings tab behavior a corresponding checkmark will appear, but this can not be done.Own VPN server on VPS/VDS hosting
What is a VPS/VDS server?
Setting up a VPN server







Installing and running the main script



Client installation for Windows 7/8/10/XP and Android




What if something went wrong


Connection errors
If everything worked, the sites are stupid and open intermittently


We let traffic through a proxy without any settings at all


How to allow only certain sites through the proxy



Shortcut for automatic connection




 Live Journal
Live Journal Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter
