Anolyte neutral anch.

  The Aquamed installation is intended for preparation of highly effective, environmentally safe and cost-effective disinfecting and washing solutions. It is a reliable and safe alternative to traditional disinfectants and detergents. "Aquamed" allows you to get rid of the problems of the acquisition, transportation, storage and accounting of disinfectants. At any time you will have as much disinfectant solution as you need! The installation was developed in conjunction with the Department of General Hygiene and Ecology of the Voronezh State Medical University and is intended for the electrochemical conversion of water-salt solutions of chlorides into a metastable activated disinfectant solution - neutral anolyte (registry. Certificate No. 08-33-0.232467), which contains the active substances represented by the products of anodic oxidation of water hydrogen and sodium chloride (HClO, HClO2, ClO2, H2 O2, HO2, O3, O2, HO). The department, together with the Vitebsk OCHEiOZ, the Republican Scientific and Research Center for Hygiene and the Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology, has established the high bactericidal, tuberculocidal, virucidal and fungicidal activity of the neutral anolyte, which meets the requirements of SanPiN 21-112-99 for safety and efficacy of disinfectants. Neutral Anolyte is intended for disinfection in medical and preventive and pharmaceutical institutions, trade enterprises, public catering and market entities, hotels and hostels, as well as for disinfection of swimming pool water in accordance with instructions approved and registered with the Ministry of Health. Neutral anolyte, having high biocidal activity, is environmentally friendly at the same time, does not accumulate in the environment, is produced from accessible and cheap components. Safety is given to the anolyte by a low concentration of active substances, and environmental friendliness is its natural property to relax spontaneously without the formation of toxic xenobiotic compounds, and neutralization after use is not required. For the operation of the installation, a pressure source of drinking water, table salt and a voltage of ~ 220V are required.
The use of the Aquamed installation is economically viable. For example, to prepare 200 liters of neutral anolyte, it is necessary to spend 1 kg of sodium chloride and 1 kW of electricity, i.e. the current cost of preparing 1 liter of neutral anolyte is about 1 ruble. Neutral anolyteobtained at the installation "Aquamed", in terms of application superior to a similar solution prepared at the installation of domestic production of the type "BAVR" and installations of the Russian production of the type STEL, EHA-30, REDO-MT2 and others, because the effect of disinfecting objects is achieved with a lower concentration of active substances in the solution and with a shorter exposure time. At the same time, the price of the Aquamed installation is lower than the indicated analogues. Currently, the installation "Aquamed" successfully used dozens of medical and sanatorium institutions of the country. There is all the necessary regulatory documentation for the installation and neutral anolyte. |
INSTRUCTIONS on the use of a neutral anolyte disinfectant solution, obtained on installations like "AQUAMED" in medical and preventive organizations
INSTRUCTION was developed by Vitebsk State Medical University, Scientific Research Institute of Sanitation and Hygiene, Vitebsk Regional Center for Hygiene, Epidemiology and Public Health, Vitebsk City Center of Hygiene and Epidemiology, Scientific and Production Unitary Enterprise “AQUAPRIBOR”.
Authors: I.I. Burak, V.I. Klyuchenovich, A.Yurkevich, N.V. Zheleznyak, N.I. Miklis, L.V. Polovinkin, A.S. Ananiev, L.V. Shunko, N. Ya.Krasovsky, N.A. Tatarenko.
The INSTRUCTION is intended for personnel of health care organizations, disinfection centers, hygiene and epidemiology centers, and other institutions involved in disinfection activities.
1. General information
1.1.The neutral anolyte is a transparent liquid with a faint smell of chlorine, the main active components of which are highly active oxygen compounds of chlorine (ClO 2, HclO, NaCIO, HClO 2, NaClO 2, etc.).
1.2. A neutral anolyte disinfectant solution is obtained by electrochemical activation in Aquamed installations (TU RB 490085159.002.2003) from aqueous solutions of chlorides (NaCl, KC1, etc.) in accordance with the Operation Manual. The installation allows you to get anolyte with an active chlorine content of 200 - 400 mg / DM 3 and pH \u003d 6.2 - 7.2.
1.3. The quality control of the neutral anolyte is carried out upon commissioning of the installation and subsequently monthly in the chemical laboratory, and self-monitoring is carried out daily and when the operating mode is changed by the express method in accordance with Appendix 1.
1.4. Prepared solutions of neutral anolyte are stored in sealed containers of inert materials (glass, nylon, plastic or enameled glassware) with tightly closed or twisted lids, in a place protected from sunlight, at room temperature for no more than 5 days after preparation.
1.5. The neutral anolyte complies with regulatory indicators of the safety and effectiveness of disinfectants, according to the requirements of SanPiN 21-112-9, does not have a toxic effect on the body and belongs to low-hazard chemical compounds (hazard class 4 according to GOST 12.1.007-76). It does not have an irritating effect on the skin, to a slight degree irritates the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and eyes.
1.6. Neutral anolyte has bactericidal, tuberculocidal, virucidal and fungicidal activity. It is effective against viruses and fungi at a concentration of 250 ± 50 mg / dm 3, tuberculosis mycobacteria - 350 ± 50 mg / dm 3, other bacteria - 250 ± 50 mg / dm 3 of active chlorine.
1.7. Neutral anolyte is intended for disinfection of surfaces in rooms, dishes, underwear, overalls for personnel, toys, sanitary equipment, medical devices, cleaning equipment and materials for infections of bacterial, tuberculous, viral and fungal etiology. Disinfection modes are presented in table 1.
2.2. Surfaces in rooms (floors, walls), surfaces of appliances, appliances, furniture, cleaning equipment, sanitary equipment (sinks, toilets, bathtubs, urinals, radiators, lighting fixtures, ventilation system grilles) are uniformly moistened with anolyte in a neutral way 2 times wiping with rags with an interval of 15 minutes The consumption of anolyte neutral is 100 cm 3 per 1 m 2 of surface. Surface areas, as an object of disinfection, are determined in accordance with Appendix 5 to the Order of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus No. 165 of November 25, 2002.
2.3. Unassembled medical devices are completely immersed in a container with anolyte neutral. In the presence of cavities and channels, they are filled with a syringe, pipette or other devices, while removing air bubbles. The disinfectant solution layer above the product must be at least 1 cm.
2.4. Dinnerware is freed from food debris and completely immersed in a container with anolyte neutral at a rate of 2 dm 3 per 1 set. Laboratory glassware is immersed in anolyte neutral. The disinfectant level must be at least 1 cm higher than the immersed dishes.
2.5. Linen contaminated with biological fluids, personnel’s work clothing, dressings, and also cleaning materials are soaked in containers with anolyte neutral at a rate of 4-5 dm 3 / kg of dry material.
2.6. Toys, patient care items are completely immersed in neutral anolyte. The disinfectant layer must be at least 1 cm higher than the disinfected objects.
2.7. After disinfection is complete, objects are washed. tap water.
| Table 1 Disinfection modes of various objects with anolyte neutral (pH \u003d 6.2-7.2) |
||||
| Disinfection object | ||||
| Bacterial, viral and fungal etiology | Tuberculous etiology | |||
| Concentration, mg / DM 3 | Exposure, min | Concentration, mg / DM 3 | Exposure, min | |
| Medical devices from: -metal, glass; -plastics, rubber, etc. |
not< 200 not< 200 |
30 60 |
not< 300 not< 300 |
60 90 |
| Tableware, laboratory | not< 200 | 60 | not< 300 | 90 |
| Surfaces (floors, walls, furniture, appliances, appliances, etc.) | not< 200 | 60 | not< 300 | 90 |
| Sanitary equipment (sinks, bathtubs, toilets, heating devices, lighting fixtures, etc.) | not< 200 | 60 | not< 300 | 90 |
| Overalls for staff (bathrobe, hat, shoe covers, etc.) | not< 200 | 60 | not< 300 | 90 |
| Underwear and bedding, diapers, dressings, etc. | not< 200 | 60 | not< 300 | 90 |
| Toys | not< 200 | 60 | not< 300 | 90 |
| Patient care items (oilcloths, enemas, vessels, etc.) | not< 200 | 60 | not< 300 | 90 |
| Cleaning equipment (mops, buckets, pans, etc.) | not< 200 | 60 | not< 300 | 90 |
| Cleaning materials (rags, napkins, etc.) | not< 200 | 60 | not< 300 | 90 |
| Rubber mats | not< 200 | 60 | not< 300 | 90 |
3. Safety requirements when receiving anolyte neutral
3.1. Operation of installations upon receipt of neutral anolyte should be carried out in a separate well-ventilated area. Collect anolyte in closed containers
3.2. Personnel who have studied the Operation Manual of the Aquamed installation and have passed a medical examination in accordance with the Resolution of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus No. 33 of 08.08.2000 must be allowed to service the installation.
When working with neutral anolyte, it is necessary to protect the skin of the hands with rubber gloves. For the duration of the exposure, the containers in which the immersion treatment is carried out are tightly closed with lids.
3.3. When operating the installation, it is necessary to comply with the requirements set forth in GOST 12.2.025. Attendants should monitor the tightness of the connections and the condition of the equipment, cleanliness and order in the room. When working with anolyte neutral, you must follow the rules of personal hygiene. It is forbidden to smoke, drink and eat food in the workplace. After work, wash your face and hands with soap.
3.4. Neutral anolyte must be stored separately from medicines.
4.1. In case of violations of labor protection rules when working with anolyte neutral, personnel may develop acute poisoning, the signs of which are: redness and itching of the skin; headache.
4.2. If there are signs of acute poisoning, it is necessary to: if possible, inhale in pairs a 2% solution of drinking soda (1 teaspoon per glass of water); see a doctor.
4.3. If neutral anolyte gets into the eyes, they should be washed with plenty of water and consult a doctor; on the skin of the hands, wash them with water and grease with a softening cream.
5. The list of possible errors in obtaining and using anolyte neutral and ways to eliminate them
5.3. In violation of the disinfection regime (reduced chlorine concentration or exposure), the biocidal activity of the neutral anolyte decreases.
Annex 1
to “INSTRUCTIONS on the use of a neutral anolyte disinfectant solution, obtained at the AQUAMED-type plants manufactured by ChNPUP“ Akvapribor ”(Gomel, Republic of Belarus) in medical and preventive organizations.
Anolyte quality control methods
1. Sampling
When sampling for quality control, the following conditions must be observed:
the sample volume of the anolyte to determine the content of active chlorine should not be less than 500 cm 3 (in accordance with GOST 18190-77);
the sample container must be airtight, made of inert material and completely filled.
2. Determination of active chlorine
2.1. Determination of active chlorine content by iodometric titration method in accordance with GOST 18190-72 “Drinking water. Methods for determination of residual active chlorine. "
2.1.1. Equipment, materials and reagents:
Laboratory glassware according to GOST 1770-74 and GOST 20292-74 with a capacity: volumetric flasks 100 and 1000 cm 3; pipettes without division 5, 10, 25 cm 3; microburette 5 cm 3; conical flasks with ground stoppers with a capacity of 250 cm 3 in accordance with GOST 25336-82;
Distilled water according to GOST 6709-72;
Sulfuric acid according to GOST 4204-77;
Potassium dichromate according to GOST 4220-75;
Soluble starch according to GOST 10163-76;
Sodium thiosulfate.
All reagents used in the analysis must be of pure qualification for analysis (analytical grade).
2.1.2. Preparation for analysis:
a) preparation of a 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate solution: 25 g of sodium thiosulfate are dissolved in freshly boiled and cooled distilled water and the volume is adjusted to 1 dm 3 in a volumetric flask;
b) preparation of a 0 1 mol / dm 3 potassium dichromate solution: 4.904 g of potassium dichromate, weighed to an accuracy of +0,0002 g, recrystallized and dried at 180 ° C to constant weight, dissolved in distilled water and adjusted to 1 dm 3;
c) preparation of 1 mol / dm 3 of sulfuric acid solution: carefully 28 cm 3 of concentrated sulfuric acid, add to 750 cm 3 of distilled water in small portions, cool and adjust the volume to 1 d 3;
g) preparation of a 0.5% starch solution: 0.5 g of starch is mixed with a small volume of distilled water, poured into 100 cm 3 of boiling distilled water and boiled for several minutes;
d) preparation of a 10% solution of potassium iodide: 10 g of potassium iodide are dissolved in distilled water and the volume is adjusted to 100 cm;
f) determination of the correction coefficient of the sodium thiosulfate solution: 10 cm 3 of a 10% potassium iodide solution are placed in a 250 cm 3 conical flask, 20 cm 3 1 mol / dm 3 sulfuric acid solution and 10 cm 3 0.1 mol / dm 3 potassium dichromate solution are added . Stir and place the flask in a dark place for 5 minutes. The liberated iodine is titrated with 0.1 mol / dm 3 sodium thiosulfate solution in the presence of 1 cm 3 of starch until a turquoise color appears, which lasts at least 30 s. The correction factor (K) is calculated by the formula:
and where a is the volume of sodium thiosulfate spent on titration, cm 3.
2.1.3. Determination process: 5 cm 3 of 10% potassium iodide solution, 50 cm 3 1 mol / dm 3 sulfuric acid solution and 10 cm 3 anolyte are introduced into a conical flask with a ground stopper. The contents of the flask are mixed and placed in a dark place for 3-5 minutes. The liberated iodine is titrated with a 0.1 mol / dm sodium thiosulfate solution until a light yellow color appears, after which 1 cm 3 of a 0.5% starch solution is added and titrated until the blue color disappears. The concentration of active chlorine (C ah, mg / DM 3) is calculated by the formula:
C ah \u003d (V * K * 35.46 * 1000 * 0.1) / 10
V is the volume of 0.1 mol / dm 3 of a sodium thiosulfate solution used for titration, cm 3; K is the correction factor for the molar concentration of the equivalent of a sodium thiosulfate solution; 10 - sample volume of anolyte taken for analysis, cm 3; 0.1 - molarity of sodium thiosulfate solution; 35.46 - the content of active chlorine corresponding to 1 cm 3 1 mol / DM 3 sodium thiosulfate solution.
2.2. Determination of active chlorine by the express method using indicator paper.
2 2.1. Equipment, materials and reagents:
Indicator paper "Millichlor";
Color scale.
2.2.2. Definition: dip a strip of test paper into the test solution, put it on a white waterproof surface, and after 30-40 s compare the color of the strip with a colored scale.
2.3. Determination of active chlorine by the express method with potassium iodide.
2.3.1. Equipment, materials and reagents:
Crystals of potassium iodide (KI) according to GOST 4232-74, chemically pure;
- "eye" spoon;
Color scale.
2.3.2. Definition: fill 1/2 of the tube with anolyte, add 1 "eye" spoon (5 mg) of potassium iodide, mix, compare with the color scale.
3. Determination of pH
3.1. Determination of the pH of the anolyte is carried out by the potentiometric method on the ionomer in accordance with the instructions attached to the device.
3.2. Determination of pH by express method using universal indicator paper.
3.2.1. Equipment, materials and reagents:
Standard scale.
3.2.2. Definition: immerse a strip of test paper in the test solution, then remove it and immediately compare the resulting color with a standard scale.
INSTRUCTIONS for the use of neutral anolyte obtained on installations like "AQUAMED" for disinfection of swimming pools.
Authors: I.I. Burak, A.B. Yurkevich, L.V. Polovinkin, Ananiev AC, Sedunov V.I., Vorokhobko CA, N.I. Miklis, N.V. Tkacheva, O.A. Kozyrevich, N.A. Tatarenko.
The INSTRUCTION is intended for medical and technical personnel of the swimming pool, hygiene and epidemiology centers, disinfection centers and other institutions involved in disinfection activities.
1. General information
1.1. Neutral anolyte is a transparent liquid with a slight smell of chlorine, the main active components of which are highly active oxygen compounds of chlorine (ClO 2, HclO, NaClO, HClO 2, NaClO 2, etc.).
1.2. Anolyte neutral complies with regulatory indicators of safety and effectiveness of disinfectants for disinfecting swimming pool water, according to the requirements of SanPiN 21-112-99 (p. 1.3, 2.3), does not have a toxic effect on the body and belongs to low-hazard chemical compounds (hazard class 4 according to GOST 12.1.007-76). It does not have an irritating effect on the skin, to a slight degree irritates the mucous membranes, membranes of the upper respiratory tract and eyes.
1.3. Anolyte neutral has bactericidal, tuberculocidal, virucidal and fungicidal activity.
1.4. These instructions regulate the use of neutral anolyte, obtained at Aquamed installations, as a disinfectant for disinfecting swimming pool water, preventive disinfection of rooms and equipment, disinfection of a pool bath after draining and mechanical cleaning. Neutral anolyte is a chlorine-containing substance, characterized by physicochemical properties that allow it to be used as a substitute for chlorine-containing preparations used to disinfect pool water.
1.5. The instructions regulate the quality control of anolyte neutral in the content of active chlorine, the use of anolyte for disinfection of water, premises and equipment of the pool and the monitoring of the effectiveness of disinfection.
1.6. The main documents regulating personal hygiene measures, sanitary-hygienic, anti-epidemic and sanitary-technical measures during the operation of swimming, swimming and sports swimming pools are SanPiN "Hygienic requirements for the design, operation and quality of swimming pools" No. 2.1.2.10-39- 2002.
1.7. Water disinfection, preventive disinfection of rooms and equipment, pool bath disinfection is carried out by specially trained pool personnel or local disinfectants on a contractual basis with systematic laboratory monitoring at the production laboratory with regular at least 1 time per month and according to epidemiological indications by the state sanitary inspection.
1.8. Responsibility for compliance with the sanitary-hygienic regime of operation of swimming pools and the use of neutral anolyte as a disinfectant lies with the administration of the pool.
2. Preparation of a neutral anolyte disinfectant solution.
2.1. A neutral anolyte disinfectant solution is obtained by electrochemical activation in Aquamed units (TU RB 490085159.002-2003) from aqueous solutions of chlorides (NaCl, KC1, etc.) in accordance with the Passport AGPTZ.293.000 PS. The installation allows you to get a neutral anolyte with an active chlorine content of 200 - 2000 mg / DM 3 and pH \u003d 6.2 - 7.2.
2.2. The prepared solution of neutral anolyte is pre-accumulated and stored in a separate sealed container of chlorine-resistant material (plexiglass, polyethylene, vinyl plastic, polyvinyl chloride, etc.) at room temperature for no more than 5 days after preparation.
2.3. The quality control of anolyte neutral is carried out upon commissioning of the installation and subsequently monthly in the chemical laboratory, and self-monitoring is carried out daily and when the operating mode is changed by the express method in accordance with clauses 3.3 and 3.4.
2.4. Precautions when working with anolyte neutral are described in the passport for the installation "Aquamed".
3.1. Sampling is carried out in a sealed container of inert material, which is completely filled, the anolyte sample volume for determining the active chlorine content must be at least 500 cm 3 (in accordance with GOST 18190-77);
3.2. Determination of active chlorine.
Color scale.
3.3.2. Definition progress:
Measured glass laboratory glassware in accordance with GOST 1770-74 and GOST 20292-74 with a capacity of: test tubes 15 cm 3.
Crystals of potassium iodide (Kl) according to GOST 4232-74, chemically pure;
- "eye" spoon;
Color scale.
4. Chlorination of the pool with anolyte neutral.
4.1. Chlorination of pool water with anolyte, like any other chlorine-containing preparation, should be based on a preliminary determination of the chlorine absorption of water, calculation of the working dose of anolyte introduced into the pool water, and determination of the concentration of residual chlorine in the water. A constant concentration of residual chlorine in the sports pool should be maintained at the level of 0.3 - 0.5 mg / l, in the rest - 0.5 - 0.7 mg / l.
In the pool bath for children 1-6 years old, the content of free residual chlorine is allowed at the level of 0.1 - 0.3 mg / l in the absence of coliphages in the water.
4.2. Over a long period (more than 2 hours), an increased content of residual free chlorine is allowed up to 1.5 mg / l, bound up to 2 mg / l. By the beginning of the reception of visitors, the concentration of residual chlorine should not exceed the standard level.
4.3. During daily cleaning, the equipment and surfaces of the toilet, shower rooms, changing rooms, walkways, benches, door handles, handrails, rugs, etc. are disinfected with neutral anolyte with a residual chlorine concentration of 200 mg / l by two times rubbing with a rag with a disinfectant flow rate of 200 ml per 1 sq. m at the surface.
General cleaning of all rooms with subsequent disinfection is carried out at least 1 time per month.
Disinfection of the bath after draining the water and mechanical cleaning is carried out by neutral anolyte with an active chlorine concentration of 200 mg / l by double irrigation with a disinfectant flow rate of 200 ml per 1 sq. m surface. The disinfectant is washed off with hot water no earlier than 1 hour after its application.
4.4. During operation of the pool, neutral anolyte is added to the circulation system continuously or periodically using an ejector connected to the storage tank.
4.5. Determination of chlorine absorption by water of anolyte neutral chlorine. The equipment, materials and reagents are the same as those used to control the concentration of residual chlorine in the pool water (section 5.3).
Three liter flasks are poured per liter of pool water and anolyte is added in volumes containing 1, 2, 3 mg of active chlorine, respectively, in the first, second and third samples. The contents of the flasks are thoroughly mixed, aged for 30 minutes and the amount of residual chlorine is determined by the iodometric method. Chlorine demand is calculated taking into account the chlorine absorption of water and the dose of residual chlorine. Recalculate the volume of the anolyte on the volume of the pool and enter its required amount using a dispenser.
Example: suppose that the working dose of anolyte, taking into account the chlorine needs of water, was 2 mg / l of active chlorine, or in terms of the volume of anolyte containing 200 mg / l of active chlorine, 10 ml of anolyte per 1 liter of water, or 10 l per 1 cubic meter. m of water. If the volume of the pool is 1000 cubic meters. m, you need anolyte 10 cubic meters. m
5. Monitoring the effectiveness of disinfection of pool water with anolyte neutral
5.1. The concentration of residual active chlorine is checked in the pool water every 2 hours.
5.2. Water sampling is carried out in at least 2 points (in shallow and deep parts).
5.3. Determination of residual chlorine is carried out according to GOST 18190-72 by the iodometric method.
6. Signs of poisoning and first aid
6.1. In case of violation of labor protection rules when working with anolyte neutral, personnel may develop acute poisoning, the signs of which are:
respiratory irritation (sore nose and nasopharynx, acute persistent cough, nasal discharge);
irritation of the mucous membranes of the eyes (burning, pain, itching, profuse lacrimation);
redness and itching of the skin; I
headache.
6.2. When signs of acute poisoning appear:
urgently take the victim to a well-ventilated area or to fresh air;
provide him with peace and warming;
give a warm drink (milk with mineral alkaline water or drinking soda);
if possible, inhale in pairs a 2% solution of drinking soda (1 teaspoon per glass of water); consult a doctor.
6.3. If neutral anolyte gets into the eyes, they should be washed with plenty of water and consult a doctor; on the skin of the hands - wash them with water and lubricate with a softening cream.
7. The list of possible errors in the preparation and use of anolyte neutral
7.1. With the wrong choice of the dose of sodium chloride, increased or reduced specific consumption of electricity, anolyte can be obtained with an insufficient concentration of active chlorine and other active substances, as well as with an acidic or alkaline reaction of the medium.
7.2. In case of violation of the method of using anolyte neutral (uneven wetting of the surfaces, incomplete immersion or soaking), the biocidal activity of the disinfectant may decrease.
7.3. In violation of the disinfection regime (reduced chlorine concentration or exposure), the biocidal activity of the neutral anolyte decreases.
7.4. When using anolyte with an acid reaction, corrosion of metal products is possible. To reduce the corrosion ability when processing metal products, only neutral anolyte should be used, and if necessary, corrosion inhibitors (0.14% sodium oleate solution) should be used.
INSTRUCTIONS on the use of neutral anolyte obtained on installations like "AQUAMED" for the disinfection of trade enterprises, public catering and market entities.
INSTRUCTION developed by Vitebsk State Medical University, Republican Scientific and Practical Center for Hygiene, Vitebsk Regional Center for Hygiene, Epidemiology and Public Health, Private Scientific-Production Unitary Enterprise "AQUAPRIBOR", Gomel.
Authors: I.I. Burak, A. B. Yurkevich, L. V. Poloviikin, Ananiev AC, T. N. Bondareva, P. V. Shelemey, N. Ya. Krasovsky, N. I. Miklis, N. A. . Tatarenko.
The INSTRUCTION is intended for personnel of trade enterprises, public catering and market entities, as well as specialists of disinfection centers, hygiene and epidemiology centers and other institutions involved in disinfection activities.
1. General information
1.1. A neutral anolyte disinfectant solution is obtained by electrochemical activation in Aquamed units (TU RB 490085159.002.2003) from aqueous solutions of chlorides (NaCl, KC1, etc.) in accordance with the Operation Manual. The installation allows you to get anolyte with an active chlorine content of 200 - 400 mg / DM 3 and pH \u003d 6.2-7.2.
1.2. Neutral anolyte is a transparent liquid with a faint smell of chlorine, the main active components of which are highly active oxygen compounds of chlorine (ClO 2, HclO, NaClO, HClO 2, NaClO 2, etc.).
1.3. The quality control of the neutral anolyte is carried out upon commissioning of the installation and subsequently monthly in the chemical laboratory, and self-monitoring - daily and when the operating mode is changed by the express method.
1.4. Prepared solutions of neutral anolyte are stored in sealed containers of inert materials (glass, nylon, plastic or enameled glassware) with tightly closed or twisted lids, in a place protected from sunlight, at room temperature for no more than 5 days after preparation.
1.5. Anolyte neutral complies with regulatory indicators of the safety and effectiveness of disinfectants, according to the requirements of SanPiN 21-112-9; does not have a toxic effect on the body and belongs to low-hazard chemical compounds (hazard class 4 according to GOST 12.1.007-76). It does not have an irritating effect on the skin, to a slight degree irritates the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and eyes.
1.6. Anolyte neutral has a bactericidal, including tuberculocidal, activity, virucidal and fungicidal activity.
1.7. Anolyte neutral It is intended for disinfection of surfaces in rooms, dishes, industrial equipment, refrigeration equipment, technological equipment, sanitary equipment, industrial and cleaning equipment, materials, etc. for infections of bacterial, viral and fungal etiology. Disinfection modes are presented in table 1.
| Table 1 Disinfection modes of various objects of trade enterprises, public catering and market entities anolyte neutral (pH \u003d 6.2-7.2) |
||
|
Disinfection object |
Infections disinfection modes: |
|
|
bacterial, viral and fungal etiology |
||
Concentration, mg / DM 3 |
Exposure, min |
|
Inventory (trade, production) from: |
||
Metal, glass; |
||
Plastics, rubber, etc. |
||
Equipment (commercial, refrigerating, technological) from: |
||
Metal, glass; |
||
Plastics, rubber, etc. |
||
Trays, sinks, racks, trade counters from: |
||
Metal, glass; |
||
Plastics, rubber, etc. |
||
Scales, juice and drink dispensers, milk, coffee, cocoa vending machines |
||
Surfaces (floor, walls) |
||
Sanitary equipment (sinks, tanks, toilets, heaters, lighting fixtures, etc.) |
||
Cutting boards, decks |
||
Cleaning materials (mops, buckets, basins, pots, rags, napkins, etc.) |
||
2. The use of anolyte neutral
2.1. Anolyte neutral should be used once without dilution.
2.2. Surfaces in rooms (floors, walls), surfaces of production and refrigeration equipment, furniture, sanitary equipment (sinks, toilets, bathtubs, urinals, heating devices, lighting fixtures, ventilation system grilles) are uniformly moistened with anolyte in a neutral way by 2 times wiping with rags with an interval of 15 minutes Anolyte consumption is 100 cm3 per 1 m 2 of surface.
2.3. The disassembled production equipment and inventory are completely immersed in a container with anolyte neutral. In the presence of cavities and channels, they are filled with a syringe, pipette or other devices, while removing air bubbles. The layer of disinfectant solution above the product must be at least 1 cm.
2.4. The dishes are completely immersed in a container with anolyte neutral. The disinfectant level above the dishes must be at least 1 cm.
2.5. Harvesting materials are completely immersed in neutral anolyte at the rate of 4 dm3 / kg of dry material.
2.6. After disinfection is completed, the objects are washed with tap water for 1-3 minutes.
2.4 Precautions when working with neutral anolyte are described in the passport for the installation "Aquamed".
3. Quality control methods of anolyte neutral.
3.1. Sampling is carried out in a sealed container of inert material, which is completely filled, the anolyte sample volume for determining the active chlorine content must be at least 500 cm3 (in accordance with GOST 18190-77);
3.2 Determination of active chlorine
3.2.1. Determination of active chlorine content by iodometric titration method in accordance with GOST 18190-72 “Drinking water. Methods for determination of residual active chlorine. "
3.3. Determination of active chlorine by the express method using indicator paper.
3.3.1. Equipment, materials and reagents:
Indicator strips DESICONT-NA-01-P-150 NPF Vinar;
Color scale.
3.3.2. Definition progress:
dip the indicator strip in the test solution, put it on a white waterproof surface and after 60 s compare the color of the strip with a color scale.
3.4. Determination of active chlorine by the express method with potassium iodide. 3.4.1. Equipment, materials and reagents:
Measured glass laboratory glassware in accordance with GOST 1770-74 and GOST 20292-74 with a capacity of: test tubes 15 cm 3.
Crystals of potassium iodide (Kl) according to GOST 4232-74, chemically pure;
- "eye" spoon;
Color scale.
3.4.2. Progress of determination: fill 1/2 of the tube with anolyte, add 1 "eye" spoon (5 mg) of potassium iodide, mix, compare with the color scale.
3.5. PH determination
3.5.1. Determination of the pH of the anolyte is carried out by the potentiometric method on the ionomer in accordance with the instructions attached to the device.
3.6. Determination of pH by express method using universal indicator paper.
3.6.1. Equipment, materials and reagents:
Universal indicator paper;
Standard scale.
3.6.2. Definition: immerse a strip of test paper in the test solution, then remove it and immediately compare the color obtained with the standard scale.
4. Signs of poisoning and first aid
4.1. In case of violation of labor protection rules when working with anolyte neutral atpersonnel may develop acute poisoning, the signs of which are:
respiratory irritation (sore nose and nasopharynx, acute persistent cough, nasal discharge);
irritation of the mucous membranes of the eyes (burning, pain, itching, profuse lacrimation);
redness and itching of the skin;
headache.
4.2. When signs of acute poisoning appear:
urgently take the victim to a well-ventilated area or to fresh air;
provide him with peace and warming;
give a warm drink (milk with mineral alkaline water or drinking soda);
if possible, inhale in pairs a 2% solution of baking soda, a teaspoon in a glass of water);
see a doctor.
4.3. If neutral anolyte gets into the eyes, they should be washed with plenty of water and consult a doctor; on the skin of the hands - wash them with water and lubricate with a softening cream.
5. The list of possible errors in the preparation and use of anolyte neutral
5.1. With the wrong choice of the dose of sodium chloride, increased or reduced specific consumption of electricity, anolyte can be obtained with an insufficient concentration of active chlorine and other active substances, as well as with an acidic or alkaline reaction of the medium.
5.2. In case of violation of the method of using anolyte neutral (uneven wetting of the surfaces, incomplete immersion or soaking), the biocidal activity of the disinfectant may decrease.
5.3. If the disinfection regimen is violated (reduced chlorine concentration or exposure), the biocodal activity of the neutral anolyte decreases.
5.4. When using anolyte with an acid reaction, corrosion of metal products is possible. To reduce the corrosion ability when processing metal products, only neutral anolyte should be used, and if necessary, corrosion inhibitors (0.14% sodium oleate solution) should be used.
reference Information
The product is not only an environmentally friendly and highly effective means of disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization of medical devices, but also an antiseptic that is used to apply on damaged skin, mucous membranes, wounds in order to prevent the development of local infections and sepsis.
Anolyte has a universal spectrum of action, i.e. It has a depressing effect on all large groups of microbes (bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoa), without harming human tissue cells. Therefore, anolyte can be used orally for inflammatory processes in the body.
The product has a LONG DURATION OF ACTION (6 MONTHS), low salinity (0.3 - 0.5 g / l) with a slight smell of chlorine and a high redox potential.
Dosage: for external use, the concentration of anolyte is up to 100%, for internal use - dilute in a ratio of 50% / 50%
Description
Anolyte disinfectant is an environmentally friendly electrochemically activated solution for universal use: for disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning, sterilization and treatment. Unlike traditional disinfecting and sterilizing solutions, such as glutaraldehyde, formaldehyde, chloramine, sodium hypochlorite, dichloroisocyanurates, peracetic acid, quaternary ammonium compounds (HOURs), heavy metal compounds and other synthetic biocidal substances, the active components of ANOLIT disinfectant are not xenobiotic substances and do not have a harmful effect on the human body and warm-blooded animals. Antimicrobial substances in the ANOLIT disinfectant are represented by a biocatalytically active low-concentrated mixture of components of active chlorine and inorganic metastable peroxide compounds, which are usually synthesized in the human body and warm-blooded animals, specialized electrochemically active cell enzymes and are involved in the neutralization of harmful and foreign phagocytes in the body. The metastable mixture of oxidants in the disinfectant ANOLIT is the most effective of all known means of destroying microorganisms, since it has many spontaneously realized opportunities for irreversible disruption of the vital functions of biopolymers of microorganisms at the level of electron transfer reactions. According to the mechanism of biocidal action, an electrochemically activated solution (ANOLIT disinfectant) is similar to a gas plasma, and its degradation products are starting materials, i.e. low mineralized water. Anolyte in terms of acute toxicity when introduced into the stomach and applied to the skin belongs to the 4th class of low-hazard substances according to GOST 12.1.007.
An environmentally friendly electrochemically activated disinfectant ANOLYT has the life time required for the disinfection procedure. After use, it spontaneously degrades without the formation of toxic xenobiotic compounds and does not require neutralization before draining into the sewer. The neutral disinfectant ANOLIT synthesized in ANOLIT devices is not only an environmentally friendly and highly effective means of disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization of medical devices, but also an antiseptic that is used to apply on damaged and intact skin, mucous membranes, cavities and wounds in order to prevent development local infectious lesions and sepsis.
The electrochemically activated neutral disinfectant ANOLIT has a universal spectrum of action, i.e. has a damaging effect on all large systematic groups of microbes (bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoa) without harming the cells of human tissues and other higher organisms, i.e. somatic animal cells as part of a multicellular system.
ANOLIT neutral disinfectant is a solution of a fundamentally new type, which has a unique biocidal effect and combines at the same time washing, disinfecting and sterilizing properties. The activated disinfectant ANOLIT obtained in ANOLIT devices destroys pathogens of both bacterial and viral and fungal etiology (Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and E. coli, hepatitis B viruses, poliomyelitis, HIV, adenoviruses, tuberculosis pathogens, salmonellosis and dermatitis. ) In its effectiveness, the ANOLIT disinfectant significantly exceeds such known disinfectants as chloramine, sodium hypochlorite, etc.
Positive results have been obtained on the destruction of pathogens of plague and anthrax with disinfectants ANOLYT. The effectiveness of the use of the solutions synthesized in the ANOLIT installations for washing military equipment and equipment from toxic substances with simultaneous degassing, as well as from toxic components of rocket fuel with the decay of these components into non-toxic simple compounds, has been experimentally confirmed.
The fundamental difference between the disinfectant Anolyte
from stable biocidal substances
|
Name of indicator |
Means ANOLYT |
|
|
Active substances |
HClO, ClO ·, ClO -, Cl ·, HO 2 ·, HO 2, HO ·, H ·, H 2 O 2, O 3, O 2 ·, 1 O 2, O · |
|
|
Active substance concentration |
||
|
Antimicrobial activity: |
||
|
Bacteria |
||
|
Causative agents of tuberculosis |
||
|
Biocompatibility |
||
|
Environmental Safety |
||
|
Washing (cleansing) ability |
||
|
Total mineralization of the working solution |
||
|
Allergenic effect |
||
|
The effect of "wet walls" after processing |
||
|
Certified Applications: |
||
|
Disinfection |
||
|
Pre-sterilization cleaning |
||
|
Sterilization |
||
|
Certified applications for disinfection: |
||
|
The surface |
||
|
Medical Products |
||
|
Heat lab tools |
||
|
Flexible endoscopes |
||
|
Dentistry |
||
|
Skin, surgeon's hands |
||
|
Inventory |
||
|
Meat industry equipment |
||
|
Equipment for the dairy industry |
||
|
Swimming Pool Water |
||
|
Waste water of tuberculosis dispensaries |
||
|
Vegetables and fruits during storage |
||
|
The preservation time of the biocidal properties of the solution |
More than 3 months |
6 months |
Redox potential of anolyte can reach -1200 mV
ANOLYT kills bacterial pathogens of fungal and viral infections and is superior in its effectiveness to chemical disinfectants such as chloramine and sodium hypochlorite. At the same time, the cost of 1 liter of it is much cheaper than a liter of a 3% solution of chloramine, sodium hypochlorite solution of Presept solution from Jonson & Jonson.
When draining ANOLYTE into the sewer, it does not need to be neutralized. Parallel purchase of detergents, sterilizers and disinfectants is not required, the costs of their delivery and storage are excluded.
Fields of application of anolyte:
Disinfection of various surfaces in the premises (floors, walls, patient care items, medical equipment, etc.)
· Disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization of medical devices, disinfection of the skin, hands of the surgeon;
· Washing, disinfecting and bleaching;
· Disinfection of beekeeping facilities and treatment of bees,
· Washing from contamination of pharmaceutical dishes;
disinfection:
· Equipment for meat and dairy industry,
· At public utilities, in hotels and hairdressers,
· Swimming pool water,
· Various objects in baths and saunas,
· Fruits and vegetables during storage,
Disinfection wastewater tuberculosis dispensaries and in the system of the Ministry of Internal Affairs,
· Washing of military equipment and equipment from poisonous substances with their simultaneous degassing, as well as from toxic components of rocket fuel with the decay of these components into non-toxic simple compounds.
Among the main advantages are the following:
- Anolyte ANK proved to be the most powerful and most versatile of all known antimicrobial liquid agents with the lowest toxicity and complete environmental safety.
- The experience of many years of practical use of ANK anolyte in hospitals confirmed the complete absence of the emergence of microorganism strains resistant to ANK anolyte.
- STEL plants for the production of ANK anolyte with PEM-3 electrochemical reactors provided thousands of medical facilities with inexpensive, highly effective and safe antimicrobial solutions for patients, staff and the environment.
- Currently, anolyte ANK is recognized as a therapeutic agent (antiseptic) for the treatment of skin, mucous membranes, purulent wounds and other purposes. Received the corresponding Pharmacopoeia article.
Redox potential, preparation of anolyte and catholyte


Redox potential (ORP) also called redox potential(from the English RedOx - Reduction / Oxidation), characterizes the ability of a chemical substance to attach and donate electrons in redox reactions, i.e. reactions associated with the attachment or transfer of electrons, and is expressed in millivolts.
During oxidative or reduction reactions, the electric potential of the oxidized or reduced substance also changes: one substance, giving up its electrons and charging positively, oxidizes (anolyte), another, acquiring electrons and charging negatively, - is restored (catholyte). The difference in electrical potentials between them is the redox potential (ORP).
In natural water, the ORP value ranges from -400 to +700 mV, which is determined by the totality of the oxidation and reduction processes occurring in it. Under equilibrium conditions, the ORP value characterizes the aquatic environment in a certain way, and its value allows us to draw some general conclusions about the chemical composition of water.
Oxidative processes lower the acid-base balance (pH) in the body, and reduction processes contribute to an increase in pH.
In the human body, the energy released during redox reactions is spent on maintaining homeostasis (the relative dynamic constancy of the composition and properties of the internal environment and the stability of the basic physiological functions of the body) and the regeneration of body cells, i.e. to ensure the vital processes of the body.
ORP of the internal environment of the human body, normally always ranging from -100 to -200 millivolt. ORP of drinking water usually ranges from +100 to +400 mV This is true for almost all types of drinking water - the one that flows from water taps, the one that is sold in glass and plastic bottles, the one that is obtained after treatment in reverse osmosis plants and most water treatment systems.
The activity of electrons is the most important characteristic of the internal environment of the body, almost all biologically important systems that determine the accumulation and consumption of energy contain molecular structures with separated charges, the electric field between which reaches large values.
When ordinary drinking water (with a weakly positive AFP, a weak anolyte) penetrates the tissues of the body, it takes away electrons from the cells and tissues that are 80 to 90% water. As a result of this, the biological structures of the body (cell membranes, organelles of cells, nucleic acids and others) undergo oxidative destruction. Thus, the body wears out, ages, and vital organs lose their function. But these negative processes can be slowed down if water with the properties of the internal environment of the body enters the body with drink and food, i.e. possessing protective reducing properties (weak catholyte).
In the natural mineral In water, the ORP value ranges from - 400 to + 700 mV, which is determined by the combination of oxidation and reduction processes occurring in it, the presence of certain salts, metal cations, gases dissolved in it, and primarily oxygen, temperature, and pH.
Preferably The ORP of the incoming fluid and food corresponded to the ORP value of the internal environment of the body. If not, then the necessary change in the ORP of water in the body occurs due to the cost of the electrical energy of the cell membranes (the vital energy of the body). This is the cause of aging.
If the drinking water entering the body has an ORP close to the value of the ORP of the internal environment of the human body, then the electrical energy of the cell membranes is not consumed and food is immediately absorbed. If drinking water has an ORP more negative than the ORP of the internal environment of the body, then it feeds it with this energy, which is used by cells, as an energy reserve of the antioxidant defense of the body from the adverse effects of the external environment,
Depending on the ORP value, several variants of natural mineral waters are distinguished:
A) Oxidizing water:
ORP\u003e + (100 - 150) mV, with the presence of free oxygen in water, as well as trace elements with high valency (Fe 3+, Mo 6+, As 5-, V 5+, U 6+, Sr 4+, Cu 2 +, Pb 2+). Water with pronounced acidic properties is called "dead" water. Its ORP in the environment can reach + 800 + 1000 mV.
"Dead" water is used to treat and prevent colds, sore throats, and flu. Dead water has a wide range of effects on the body: it lowers blood pressure, improves sleep, and soothes the nervous system. “Dead” water dissolves stones on the teeth, stops gum bleeding, and helps treat periodontal disease. Reduces joint pain, helps with intestinal disorders.
B) Transitional redox water:
ORP from 0 to + 100 mV, unstable geochemical regime and variable content of hydrogen sulfide and oxygen. Under these conditions, both weak oxidation and weak reduction of a number of metals occur.
C) Recovery water:
ORP< 0. Типична для подземных вод, где присутствуют металлы низких степеней валентности (Fe 2+ , Mn 2+ , Mo 4+ , V 4+ , U 4+), а также сероводород. Это типично для подземных горных источников, талой воды.
Water with negative ORP values \u200b\u200bis called “living” water. "Living" water (alkaline) is an excellent stimulant, tonic, energy source, gives energy, stimulates cell regeneration, improves metabolism, and normalizes blood pressure. "Living" water is able to heal wounds, burns, ulcers (including the stomach and duodenum 12). "Living" water is used to treat and prevent osteochondrosis, atherosclerosis, prostate adenoma, polyarthritis and other diseases.
Negative ORP of drinking water gives energy to cells, organs, and systems. The electrical energy of cell membranes is not spent on the correction of the activity of electrons of water and water is immediately absorbed, because possesses biocompatibility on this parameter.
The main technology for producing these types of water is electrolysis.
ORP values, mV |
|
|
Arterial blood |
7 |
|
Deoxygenated blood |
57 |
|
The internal environment of a healthy human body |
70 |
|
Fresh juice (from the garden) |
30 - +70 |
|
Freshly squeezed juice after a day of storage |
50 - +100 |
|
Natural water in long-livers |
30 - +70 |
|
Water with microhydrin |
200 |
|
Tap water |
220 - +380 |
|
Bottled water |
210 - +400 |
|
Optimal environment for sperm motility |
130 |
|
The optimal environment for the growth of beneficial bacteria (E. coli, bifidobacteria) |
50 - -200 |
|
Mother's milk |
70 |
For all these diseases, the selectivity of the anolyte was repeated: destroying pathogenic microorganisms, it left the beneficial microflora unharmed. Moreover, it turned out that the "intellect" of the anolyte directly depends on its redox potential and manifests itself only at its specific values.
This property of the anolyte gives it a huge advantage over antibiotics, because, destroying the pathogenic flora, they also “cut out” the bacterial environment necessary for the normal existence of one organ or another, which leads to numerous diseases.
In contact with a microbial cell, the anolyte causes its death by violating the integrity of its single-layer cell wall, leakage of intracellular components, disruption of the ribosomal apparatus, coagulation of the cytoplasm, etc. In this case, the anolyte mimics the processes used by the body in the fight against bacteria, viruses, and alien and degenerated (cancerous) cells.
Which cell for the manufacture of anolyte and catholyte to choose?
Simple (stationary) models of electrolytic cells consist of an anode and a cathode and a semipermeable membrane (it is impermeable to molecules, but well permeable to ions). Such electrolyzers are filled with water and connected for a certain time to the electrical network. As a result of the passage of electric current through water, H 2 O is separated, as well as chlorine and various minerals (sodium, calcium, potassium, iron and others) contained in water, into positively and negatively charged ions.
Chlorine and the remaining oxidizing agents are collected in the anode zone - this is dead water, which has a high redox potential (up to 1200 mV) and high acidity (pH up to 2). The water of the cathode zone is living water, it is freed from chlorine, saturated with electrons (negatively charged hydrogen) and ions of minerals, and acquires a negationthe effective redox potential (up to -800 mV) and alkaline pH value 7-12.
There are also more modern electrolytic apparatuses of Russian, German and South Korean production. They have a modern design and computer control. You do not need to pour water into them - they are connected to a water tap. Thus, all drinking water can be freed from chlorine and chlorine compounds. They have built-in filters that remove chemical impurities, harmful substances and hard salts from the water. Such devices are characterized by several stages of activation, and each stage has its own indications for use.
The leader among electrolyzers is Dina Ashbah plant, the basis is Bahir modules, allowing to obtain anolyte and catholyte with the required ORP:
1) fixed settings for receiving catholyte 3 degrees of activation
For daily drinking ORP minus 50 -100 mV, pH 7.5-8.0 (recommended for children)
For daily drinking, ORP minus 100-150 mV, pH 8.0-9.0
For treatment, AFP greater than 200 mV, pH 9.0-10.0
2) fixed settings for receiving anolyte 2 degrees of activity
For internal use, ORP + 600 + 800 mV, pH 4-5
For external use, ORP + 800 + 900 mV, pH 2.5-3.5
Read more - electrochemical activation technology (ECA)
Water is the most abundant chemical compound on the planet.It is found in a variety of conditions, has many very different properties. At the same time, water can behave both as an elixir of life and as its active enemy. Man exists thanks to the water that fills him.
The latest technologies, based on research and discoveries of domestic scientists, have led to the creation of unique water treatment plants and the preparation of disinfecting water-salt solutions. These technologies are based on the principle electrochemical activation (ECA)water discovered at the beginning of the XIX century russian academician V.V. Petrov, the result is charged water.
STEL devices (at STnew ELelectrochemical activation) which are widely used nowadays not only in Russia but also around the world, can radically improve the quality of drinking water and replace expensive and dangerous disinfectants for humans with environmentally friendly water-salt solutions.
Activated solutions - this solutions obtained by electrolysis in the diaphragm of the electrolyzer. That is, we feed a weakly mineralized aqueous solution at the inlet of the electrolyzer, and at the exit from the anode chamber we obtain anolyte and, accordingly, at the exit of the cathode chamber we obtain catholyte ( catholyteand anolyte - this is living and dead water) These solutions have very interesting properties. If we talk, for example, about medicine, then anolyte is used as a disinfectant, and catholyte is used as a detergent. 

IN sTEL installationsource materials - tap water and salt ( ChloridesodiumNaCl, sodium salt of hydrochloric acid, is known in everyday life by the naming of table salt) At the output of the installation, activated solutions are synthesized - catholyteand anolyte. Wherein catholyteand anolyte- can be used not only as washing, disinfecting and sterilizing, but also for the prevention and treatment of various inflammations, human diseases. Their main advantage over traditionally used therapeutic agents is full biological compatibility and harmlessness - they do not contain chemical elements and compounds alien to the human body. At the same time, these are the most powerful of the known regulators of redox and biocatalytic processes in living organisms.
Setting STELdesigned for synthesis ecologically clean electrochemically activated solution for universal use-anolyte ANK(Anolit Nneutral / TOpure - depending on the synthesis conditions) for sterilization of medical instruments, disinfection and washing in medicine, food industry, public utilities, disinfection of drinking water.
STEL installationsirreplaceable in remote areas, garrisons and frontier posts, as well as in emergency situations - wherever prompt delivery of a large number of disinfectants is required.
Anolyteentered in the register of disinfectants approved for use on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Setting STELpurify water from microorganisms of all types and forms, microbial toxins, heavy metal ions and harmful organic compounds, and also give physiologically functional properties to water. The main process of water treatment in plants STEL is her electrochemical activationas a result, the source water acquires intracellular fluid propertiesand becomes essentially healing, anti bacterial water.
The name of the plants for the synthesis of electrochemically activated antimicrobial and detergent solutions - STEL - was first made in 1989. Two words are combined in this name - STERILITY and ELECTROCHEMISTRY. This name is attached to all types of electrochemical plants that produce washing, disinfecting and sterilizing electrochemically activated solutions.
Due to the design features, the MB element (Bahir module) is a practically non-alternative reactor in the technology of synthesis of electrochemically activated solutions. Only in this reactor can conditions be created for the simultaneous synthesis of chlorine-oxygen and hydroperoxide oxidants in higher oxidation states. It is only in this reactor that it is possible to provide conditions for the formation in the double electric layer near the anode surface of dense, electrically structured ion-hydrated shells surrounding freshly formed oxidants and preventing their rapid mutual neutralization. In this reactor alone, in the shortest possible time of fluid movement in the cathode chamber, practically all heavy metal ions can be converted into insoluble hydroxides and the catholyte can be saturated with dissolved hydrogen. Only in this reactor can the hydrogen dissolved in catholyte be made to take part in the anode reactions of the synthesis of oxidants.
The simplest water treatment technology in flow diaphragm reactors consists in the simultaneous synthesis of approximately equal volumes of catholyte and anolyte - cathode and anode treated water or solution, respectively. The perfection of the reactor in this technology is manifested in the ability to obtain the maximum possible values \u200b\u200bof the redox potential of the anolyte at the minimum pH value, as well as the minimum possible values \u200b\u200bof the redox potential of catholyte, at the lowest possible energy consumption, at the greatest possible productivity and the lowest possible mineralization of the initial solution or water. at its maximum pH. It was these conditions that were once considered to be the main ones in obtaining “living” and “dead” water, however, they were often achieved by increasing the salinity of the water and the time of its electrochemical treatment. In fact, in order to obtain electrochemically activated water - catholyte or anolyte, it is necessary to ensure that each microvolume of the treated water is in contact with the surface of the corresponding electrode that is not soluble in water, with a minimum change in water temperature (1 - 2 degrees), the minimum possible mineralization, as a rule not exceeding the salt content in ordinary drinking water and for the minimum time calculated in whole seconds or fractions thereof. It is clear that most of the apparatus for producing living and dead water produced at the beginning of the eighties, as well as apparatus for a similar purpose manufactured at the present time, did not and does not correspond to these principles.
Obtaining a disinfectant solution - an acid anolyte in STEL installations does not present any technical difficulties, however, it is impractical due to its high corrosivity and the sharp smell of chlorine. The sharp smell of chlorine can be avoided only when using ordinary drinking water without salt additives as the initial solution, however, the anolyte obtained from fresh water does not have sufficiently effective antimicrobial properties for use as a disinfectant in health facilities.
In anolyte ANK, which has a neutral pH value, active substances are mainly represented by hypochlorous acid, a small amount of hypochlorite ions, chlorine dioxide, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, and singlet oxygen. It is impossible to obtain such a mixture of oxidants chemically, however, it is formed in the human body during phagocytosis due to electrochemical reactions in the cytochrome P-450 enzyme and there is a very short time solving the problems of fighting the infection.
The specific conditions of electrochemical synthesis in the patented electrochemical reactors of STEL devices can create conditions for the long-term (from several days to two to three months) coexistence of metastable antagonistic particles in a solution. Anolyte ANK (Anolyte Neutral with the previous Cathodic treatment) is a fundamentally new object in comparison with traditional disinfectants, similar to a cold plasma, unlike, for example, a hot plasma flame of an alcohol lamp. In both cases we deal with metastable particles, to which microorganisms cannot develop resistance for fundamental reasons and whose chemical composition cannot be prepared for a thorough study of each individual component. That is why anolyte ANK with an ADV concentration of only 0.03% destroys anthrax spores in a matter of seconds, while to achieve the same result, a solution of sodium hypochlorite with an ADV concentration 150 times higher requires at least 30 minutes. These data are given from the scientific report of the Battelle Memorial Institute (USA), but in one form or another they have been confirmed by research organizations in more than 50 countries, including Russia.
- < Назад

To combat microbiological pollution in our country, more than four hundred domestic and foreign drugs are used. Such an amount of disinfectants greatly complicates the choice of the drug for each individual case. Indeed, the number of harmful microorganisms that are resistant to certain chemical compounds is increasing all the time, and the choice of disinfectants in clinics is often determined by the commercial interests of those responsible for the purchase of drugs. The result of this approach is that the drugs used do not give the proper disinfecting effect. With prolonged use of the same tool, microorganisms adapt to its action and create a risk of infection.
Our company produces special equipment with which synthesized from a salt solution by electrolysis electrochemically activated detergent and antimicrobial solution - Neutral anolyte. The AQUACHLORIN-40 device is a modern electrochemical system that is capable of synthesizing (producing) from 60 to 250 liters of Neutral Anolyte per hour (depending on version).
Neutral anolyte - is a washing, antimicrobial solution, the chemical properties of which do not allow microorganisms to develop resistance to their effects. This allows the widespread use of Neutral Anolyte as disinfection solution.
Neutral anolyte is a disinfectant (working solution), which is not difficult to obtain using the AQUACHLORIN-40 installation at the place of its operation in the required quantity.
The shelf life of the Neutral Anolyte while maintaining the disinfecting ability is 180 days.
The shelf life of a Neutral Anolyte while maintaining sterilizing ability is 10 days.
Low cost of production of the solution Neutral anolyte at the AQUACHLORIN-40 installation is an indicator of profitability and quick payback.
Neutral anolyte ANK like disinfection solution can replace more than 90% of disinfectants used in medical institutions, while ensuring a high level of disinfection.
AQUALIGHT (neutral anolyte) is primarily an effective disinfectant. This solution is able to destroy a variety of viruses, bacteria, fungi and other microorganisms. Moreover, regardless of the frequency and duration of its use, the bacteria do not develop addiction to it and the ANK Neutral Anolyte meets the requirements for disinfectants. The disinfectant has good bactericidal and anti-fungal properties, low cost. This solution for disinfection can and should be used at the locations (crowds) of people and animals, since low toxicity makes it possible to carry out disinfection in the presence of people and animals, which distinguishes it from other solutions used for disinfection. The ANK neutral anolyte is absolutely safe, environmentally friendly and completely biodegradable.
Neutral anolyte also has the properties of a detergent, washing and disinfecting any objects in the room. A high degree of sporicidalness of the disinfectant allows it to be used as a means of sterilization in centers of infectious diseases.
Neutral Anolyte Synthesized by AQUACHLORIN-40 Electrolysis Systemnon-toxic (belongs to the IV class of low-hazard compounds and to the V class of practically non-toxic substances according to the classification of K.K. Sidorov (DL 50 in the abdominal cavity more than 1000 mg / kg)), does not have a harmful effect on the environment, relaxes in time with the formation of a solution of sodium chloride in water and oxygen evolution, there is no toxicity to flora and fauna. It can be used in the presence of people with any method of application - rubbing, dipping, soaking and spraying.
- the antimicrobial agent has a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action, that is, it effectively destroys bacteria, mycobacteria, viruses, fungi and spores, regardless of the duration and frequency of use, which suggests the presence of properties that prevent microorganisms from developing resistance;
- an antimicrobial agent is safe for humans and animals both during its preparation and use, and after the end of its intended use, that is, during degradation and destructive changes under the influence of environmental factors or as a result of biodegradation processes in the human body, that is, in other words antimicrobial agent and products of its natural or artificial degradation do not contain xenobiotic substances;
- the antimicrobial agent has universality of action, that is, it has not only antimicrobial properties, but also has a washing ability, as well as the most simple to use and at the same time very inexpensive.
- has a high sporicidal activity (provides sterilization), is used for bacterial infections (including tuberculosis),viral (including hepatitis) and fungal etiology, does not cause resistance in microorganisms.
The most common and most economical way to use the AN K Neutral Anolyte is by aerosol spraying disinfection solution, in which the active substance is quickly distributed throughout the volume of the room, while creating an air environment free of pathogenic microflora. In addition, when the drug is transferred to an aerosol state, its specific surface area increases. The sprayed substance has a hundreds of thousands of times larger surface than the liquid, resulting in increased disinfectant activity.
Traditional disinfecting and sterilizing drugs are mostly xenobiotics, that is, substances that have a high degree of toxicity. In contrast, the ANK Neutral Anolyte is absolutely safe for humans and animals due to the low total concentration of active oxygen and chlorine in the solution. The ANK neutral anolyte surpasses known disinfectants in terms of destination, including those manufactured by foreign manufacturers.
Solution Neutral Anolyte ANK is used:
In medicine for the disinfection of rooms in hospitals, clinics, polyclinics, dental clinics, medical centers (including in infectious wards at the time of the stay of people);
In public places (sports halls, transport, public crowds, public toilets)
In the home (disinfection of any objects in the home, as well as fruits, vegetables, meat and other food products in order to increase shelf life)
In the Ministry of Emergency Situations (air disinfection (by spraying), disinfection of vehicles, disinfection of dumps hazardous in the epidemiological plan)
In agriculture and the agro-industrial complex (disinfection of livestock buildings and other agricultural facilities, processing plants in greenhouses to combat viral and bacterial diseases, irrigation water treatment and water treatment, disinfection of seeds and seedlings before sowing and planting, processing of finished agricultural products to increase its terms storage, silage of green feed)
In the food industry (processing of raw materials at food processing plants, for example, with the aim of disinfecting and increasing shelf life; disinfection of carcasses of livestock and birds in slaughter shops and meat processing plants; disinfection of fish and seafood)
Comparative characteristics of disinfectants

Antimicrobial activity of chlorine solutions
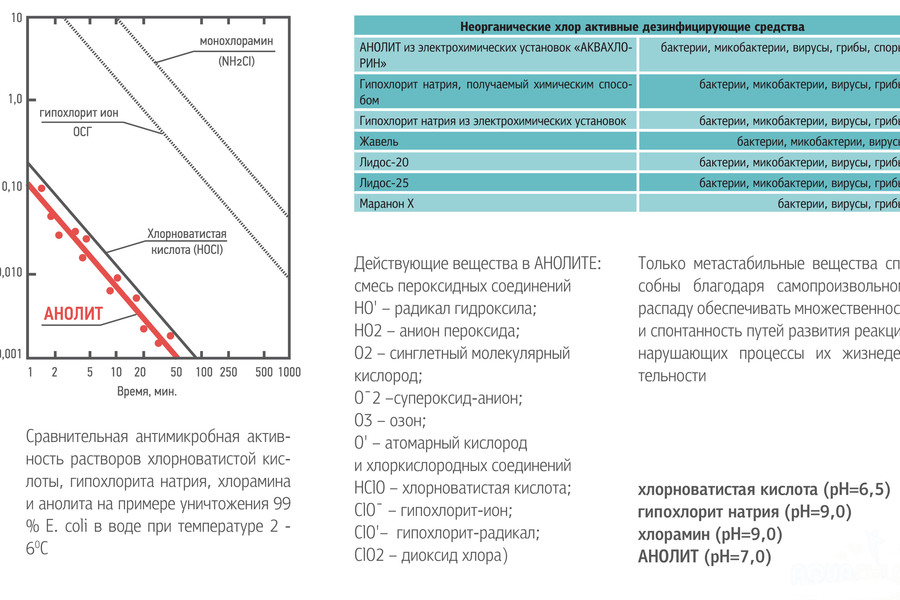
Active ingredients in the neutral anolyte ANK

The effectiveness of the neutral anolyte ANC in relation to spores

The effectiveness of the neutral anolyte ANC in relation to bacteria
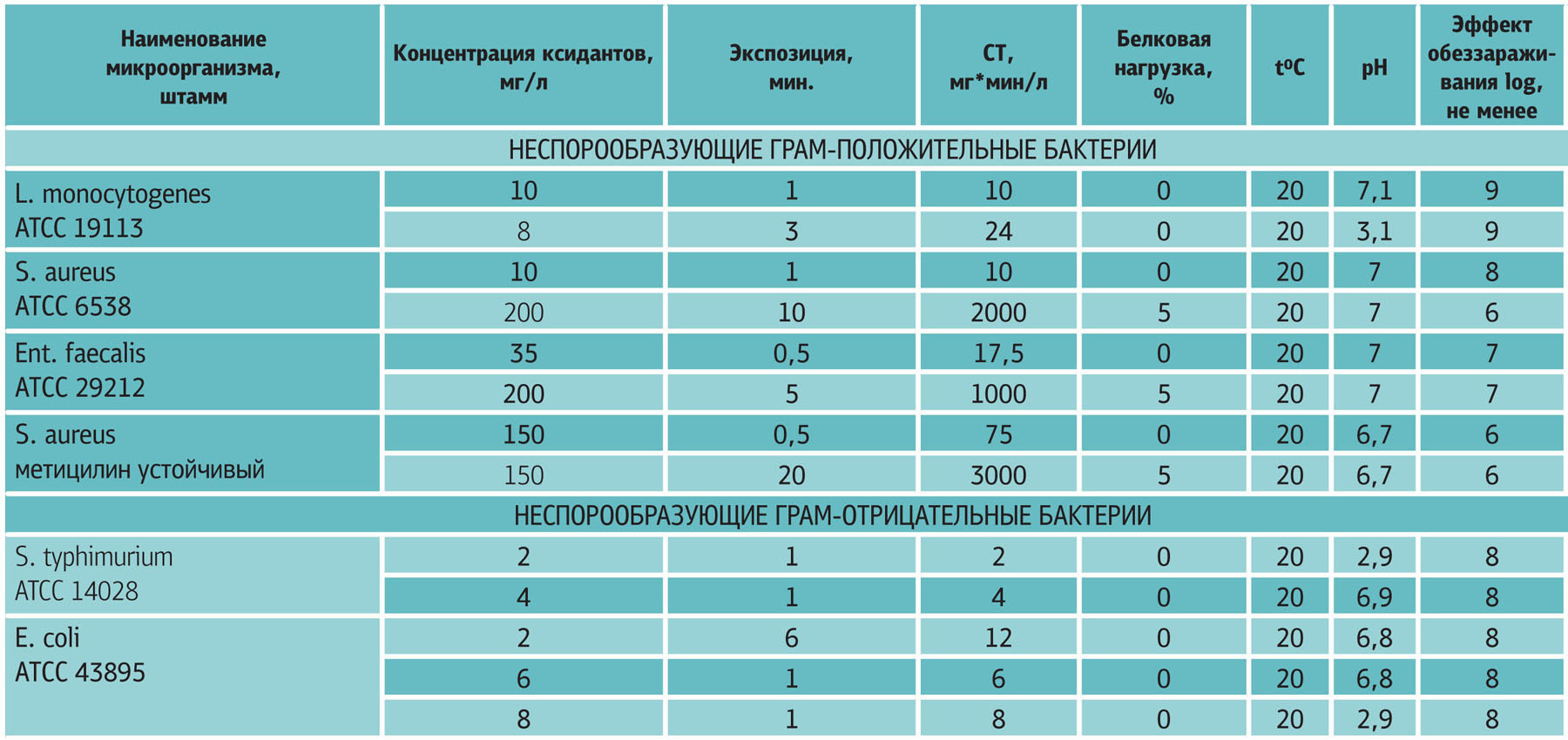
The effectiveness of the neutral anolyte ANC in relation to viruses, phages and fungi
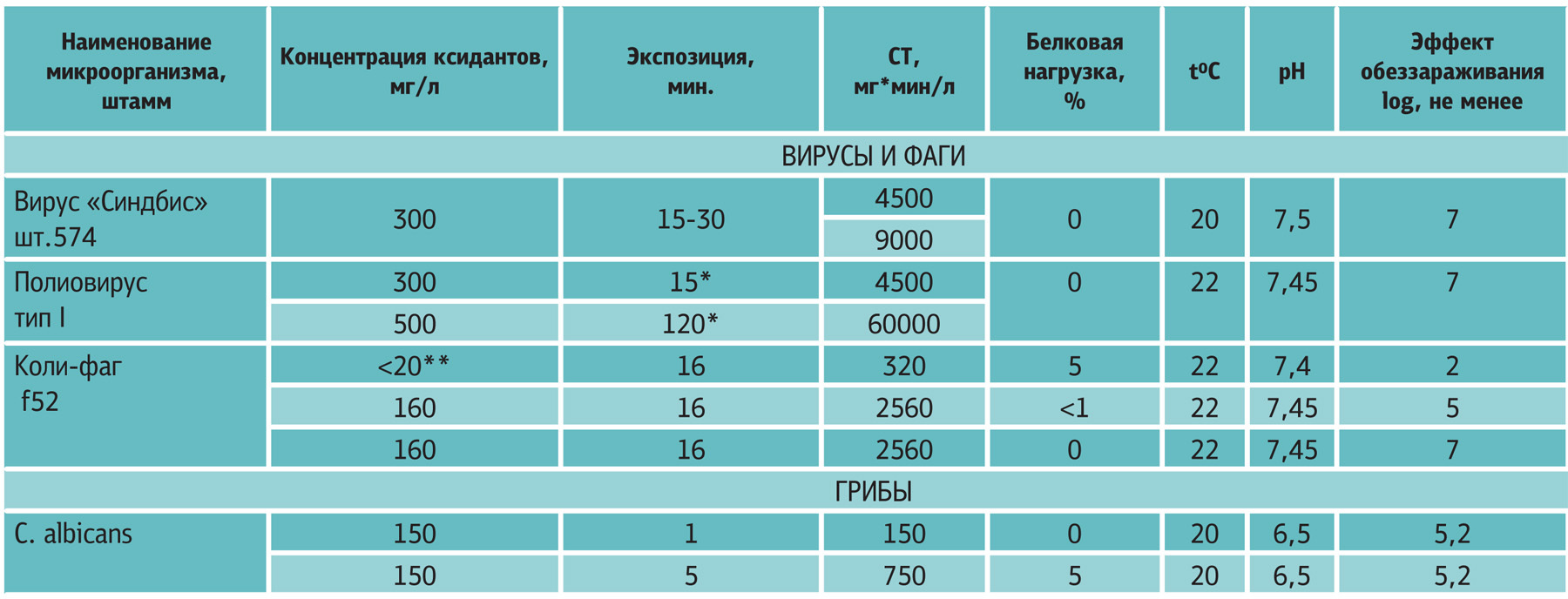
The effectiveness of the neutral anolyte ANC in relation to microbacteria

The use of ANK Neutral Anolyte in medical institutions
Hospitals. In inpatient departments of a therapeutic profile, the volume and form of use of anolyte ANK depend on the purpose of the premises, equipment, medical equipment and devices. The largest area in the therapeutic departments is wards for patients, where 2 times a day the current wet cleaning with ANK Neutral Anolyte is carried out, which includes: mopping, wiping furniture, window sills, headboards. Once or twice a month, a general cleaning of the chambers is carried out, in which, in addition to the current cleaning, the ANCs wipe the walls, lighting devices, the inner surfaces of the bedside tables, etc.
If an infectious patient is identified after isolation final disinfection in the room. Bed linen and household items used by the patient (dishes, cutlery) are soaked in the ANK Neutral Anolyte. A disinfectant is applied on the floor, walls and ceiling with a spray at the rate of 1 liter per 20 m2 of area, they also perform wet cleaning with ANK Neutral Anolyte with the wiping of furniture, window sills, beds and other equipment and inventory located in the room.
Treatment rooms. The greatest functional load in the departments of the therapeutic profile falls on treatment rooms. In them, before and after the end of the working day, the current wet cleaning is carried out with the ANC Neutral Anolyte wiping the surfaces of the treatment tables, shelves, cabinets, couches, window sills and floor. In the process, after the end of each procedure, the workplace is wiped with an ANK Neutral Anolyte, and if blood drops get on the surface, they are cleaned with a swab moistened with ANK Neutral Anolyte followed by a double rubbing of this place. Disposable syringes, needles, systems and tampons that removed blood are placed in containers with a volume of at least 10 l filled with ANK Neutral Anolyte with an oxidant concentration of 0.05%, where they must be kept for at least 1 hour.
Once a week in the treatment rooms, a general cleaning is carried out with wiping of all surfaces (ceiling, walls, objects, equipment) with ANK Neutral Anolyte, followed by irradiation with an ultraviolet bactericidal lamp.
Dining rooms, buffets. Before the next meal, they wipe the surfaces of furniture, refrigerators, processing equipment and cutting equipment in the rooms of dining rooms and buffets with ANK Neutral Anolyte. Dishes with food debris are soaked in a 0.05% ANK Neutral Anolyte for 1 hour, and then washed according to the generally accepted scheme. In addition, a general cleaning of the premises is carried out 2 times a week, during which they wipe the walls, window sills, surfaces of all objects with ANK Neutral Anolyte. Tanks for food debris and collecting dirty dishes after degreasing are sprayed with 0.05% ANK Neutral Anolyte.
Diagnostic rooms. Functional diagnostics rooms are treated with ANK Neutral Anolyte (mopping, wiping furniture, equipment surfaces, window sills) twice a day. The couches are wiped with a solution of the neutral anolyte ANK after each patient. General cleaning, in which the walls are additionally wiped with a solution of ANK Neutral Anolyte, is carried out 1 time per week.
Bathrooms In bathrooms and (or) enema rooms, 2 times a day, wet cleaning is carried out with a solution of ANK Neutral Anolyte. The bathroom after each patient is disinfected with a solution of ANK Neutral Anolyte by the method of irrigation of the inner surface. After 30 minutes, wash in the usual manner. After use, the enema tips are soaked for 30 minutes in a solution of ANK Neutral Anolyte, washed and washed with tap water and detergent, and stored in ANK Neutral Anolyte solution until next use. The surfaces of the rubber parts of the enemas after application are wiped with a solution of ANK Neutral Anolyte. After use, rubber gloves are washed with tap water and soap, soaked for 30 minutes in a solution of ANK Neutral Anolyte and dried.
Toilets. In the toilet rooms, routine cleaning with washing sinks, urinals, toilets and floors is carried out 4-6 times a day with ANK Neutral Anolyte solution. General cleaning, including all the elements of the current one with additional wiping of the water-repellent surfaces of the walls with ANK Neutral Anolyte solution, is carried out once a week.
Surgical departments. Carrying out hygienic and disinfection measures in surgical departments does not fundamentally differ from the above. However, some features related to the presence of open wound surfaces of the skin and mucous membranes, the multiplication of the microbial flora in inflammatory diseases, the possible presence of infection with anaerobic microorganisms, and the weakening of the body's resistance after extended surgical interventions should be taken into account. According to Yakovlev S.V., infectious complications develop on average in 5% of surgical patients. They significantly increase the time of recovery, the length of hospital stay of patients and the cost of treatment. The most common infections in surgery are postoperative infections (wound infections of the skin and soft tissues and intra-abdominal inflammatory processes). A feature of all nosocomial infections is the high resistance of pathogens to antibacterial drugs, primarily to penicillins, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, and the possible emergence of resistance to other antibiotics.
The greatest attention to sanitary measures is given an operating unit, including an operating room and a number of auxiliary roomswhere it is necessary to minimize the risk of introducing an exogenous infection into the wound. The use of a solution of ANK Neutral Anolyte, which does not have a smell and irritating effect, allows you to combine disinfection and certain types of cleaning the room.
It should be noted that the use of ANC for cleaning and disinfection of operating rooms with a solution of Neutral Anolyte does not preclude other measures (air purification, ultraviolet irradiation with bactericidal lamps).
Sterilization room. In the sterilization room, similar measures are carried out with the exception of the current cleaning in the process and immediately after each operation. In a sterilization room, in some cases, medical devices are sterilized with a solution of ANK Neutral Anolyte.
Premises of a strict sanitary and epidemiological regime. Sanitary and hygienic measures in the premises of the strict sanitary and epidemiological regime ( preoperative and anesthetic) consist of twice daily wet cleaning with ANK Neutral Anolyte solution with wiping of all horizontal surfaces and once a week general cleaning with ANK Neutral Anolyte solution. Moreover, in preoperativeAs a method of choice, the preparation of the surgeon's hands for surgery with ANC Neutral Anolyte solution with a concentration of oxidants of 300 mg / l can be applied by wiping or by immersion. In both cases, the hands are first washed with soap and wiped with a sterile cloth.
In anesthetic solution, ANK Neutral Anolyte is used to disinfect the outer surfaces of anesthesia devices by wiping rubber, plastic and metal parts in contact with the surfaces of the body and mucous membranes of patients, as well as gas conduits. Sterilization is carried out after removal of biological and contaminating products from the surface and lumen by washing with water and detergents and drying. Products are placed in a solution of Neutral Anolyte ANK.
Premises of a zone of limited sanitary and epidemiological regime. In the premises of the restricted regime zone (storage and preparation of blood, storage of portable equipment, plaster bandages, urgent analysis laboratory, nursing room, surgeon's room, protocol room and others) wet cleaning twice a day with ANK Neutral Anolyte solution and once a week - general cleaning with ANK Neutral Anolyte solution. In the laboratory of urgent analyzes and the room for storing and preparing blood, the routine cleaning of blood drops on the surface of the floor, furniture or equipment is carried out by wiping the contaminated places with tampons or rags moistened with ANK Neutral Anolyte solution. Slides, melangers, tubes and other containers, after use, are soaked in ANK Neutral Anolyte solution for 30 minutes, washed and disinfected in a freshly obtained ANK Neutral Anolyte solution for 30 minutes.
In dressings, all cleaning and disinfection of the premises using the ANK Neutral Anolyte solution are similar to those for operating rooms.
In the wards of the intensive care unit
in addition to daily wet cleaning twice with ANK Neutral Anolyte solution and general cleaning once a week with ANK Neutral Anolyte solution, routine cleaning is carried out when biological substances (blood, vomit, mucus and others) get onto the floor and surrounding objects by wiping the contaminated places with a rag moistened with solution Neutral Anolyte ANK. Contaminated linen, bedding is soaked in a solution of ANK Neutral Anolyte before washing for 1 hour. After-use vessels and other care items are washed with ANK Neutral Anolyte solution, followed by soaking them for disinfection in ANK Neutral Anolyte solution of the same concentration for 1 hour.
Description: the solution developed in the STEL-10N-120-01 installation for disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization, ready for use.
Production: Russia
Appointment: Anolyte ANK is intended for the disinfection of various objects (indoor surfaces, patient care items, dishes, linen, toys, sanitary equipment, cleaning material) for bacterial infections (including tuberculosis), viral (including hepatitis with a parenteral transmission mechanism, HIV- infection, poliomyelitis, adenoviruses, SARS viruses, H5N1 bird flu, herpes) and fungal (including candidiasis, dermatophytosis) etiology, as well as for disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization of ed Medical products made of glass, plastics, rubbers, metals (titanium alloys) in medical institutions. Anolyte Neutral ANK is used as a medicine as a solution for local and external use and treatment of wounds.
Composition: contains highly active oxygen compounds of chlorine and other oxidants in the form of peroxide and hydroperoxide compounds, i.e. a mixture of highly active metastable (electrochemically activated) oxidants, quantified by the equivalent of “active chlorine”. Depending on the purpose, Anolyte ANK is prepared and used with a content of a mixture of oxidants in the equivalent of active chlorine of 0.01%, 0.02%, 0.03%, 0.05% and a pH value of 7.2 to 7.5.
Consistency, properties: ANK neutral anolyte produced in the STEL-10N-120-01 installation (TU 9451-689-05834388-2006) of various models by electrochemical treatment of a solution of sodium chloride in drinking water, is a colorless transparent liquid with a faint smell of chlorine.
Packing: glass and plastic containers with a volume of 0.4 to 20 liters.
Microbiology: Anolyte ANK has antimicrobial (virucidal, bactericidal, tuberculocidal, fungicidal, sporocidal) and detergent properties. In the presence of organic contaminants (feces, blood, etc.), the disinfectant activity of Anolyte ANK is reduced.
Toxicity: "Anolyte ANK" by the degree of exposure to the body belongs to the 4th class of low-hazard substances (according to GOST 12.1.007) when introduced into the stomach, applied to the skin, has little toxicity with parenteral administration. It does not have a local irritant effect on the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes (when washing).
Application: “Anolyte ANK” disinfection is carried out by means of wiping, soaking, immersion and irrigation. Use anolyte at room temperature. Wipe disinfection can be carried out in the presence of patients.
Shelf life: 5 days if stored in a closed glass, plastic or enamelled (without damaging enamel) container at room temperature in places protected from direct sunlight.
Storage conditions: in a closed container, avoiding direct sunlight.
We have a low price for Anolyte neutral ANC .. You can buy other disinfectants wholesale and retail using the basket on our website.
I affirm: Head of department
State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision Ministry of Health of Russia
A.A. Monisov
02/14/1997
N MU-17-12
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
1. GENERAL PROVISIONS.
- The ANK neutral anolyte (hereinafter referred to as the anolyte) produced in the STEL-10N-120-01 installation (hereinafter referred to as the installation) by electrochemical treatment of a solution of sodium chloride in drinking water is a colorless transparent liquid with the smell of chlorine containing highly active oxygen compounds of chlorine, etc. .
Depending on the purpose, anolyte is prepared and used with an active chlorine content of 0.01%, 0.02%, 0.05% and a pH value of 7.2 to 8.4.
Monitoring of these parameters should be carried out during commissioning of the installation, as well as during its operation after each switching to a different operating mode (saline flow rate, current strength) to obtain anolyte with another specified (from the above) concentration of active chlorine, but not less once a month. The anolyte quality control methodology is given in Appendix 2.
Anolyte is used without dilution, once.
The anolyte has a shelf life of 5 days if stored in a closed glass, plastic or enamelled container (without damaging the enamel) at room temperature in places protected from direct sunlight. - Anolyte has antimicrobial (bactericidal, tuberculocidal, virucidal, fungicidal, sporocidal) and detergent properties.
- Anolyte is used to disinfect various objects (indoor surfaces, patient care items, dishes, linen, toys, sanitary equipment, cleaning material) for bacterial infections (including tuberculosis), viral (including hepatitis with a parenteral transmission mechanism, HIV infection ) and fungal (including candidiasis, dermatophytosis) etiology, as well as for disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization of medical devices made of glass, plastic, rubber, metals (titanium alloys).
The process of disinfection of medical devices can be combined with the process of their pre-sterilization cleaning.
2. APPLICATION OF ANOLYTE FOR DISINFECTION
- Anolyte disinfection is carried out by wiping (surfaces on the premises, sanitary equipment) and immersion (medical devices, patient care items, dishes, underwear, toys, cleaning material).
- Anolyte disinfection regimens for infectious diseases of various etiologies are presented in Table 1.
- The surfaces in the premises (floor, walls, hard furniture), sanitary equipment are wiped once or twice (with an interval of 15 minutes) with a rag abundantly dampened with anolyte. The surfaces to be treated should be evenly moistened. The rate of anolyte consumption for a single rubbing is 200 ml, for a double rubbing (total amount) - 300-400 ml per 1 m 2 of the treated surface. Heavily contaminated sanitary equipment is pre-cleaned with a ruff moistened with anolyte.
- Medical products are completely immersed in the anolyte, filled with the help of auxiliary means (syringe, pipette) cavities and channels of the products, while removing air bubbles. Detachable products are disinfected disassembled. After the end of disinfection exposure, the products are washed for 1 minute flowing drinking water or incubated in a container of water for 1 minute with the filling of cavities and channels of products with water.
- Patient care items are completely immersed in anolyte. After disinfection is completed, they are washed with running water until the smell of chlorine disappears.
- Dishes are freed from food debris and completely immersed in anolyte. The anolyte consumption rate is 2 liters per 1 set (two plates, a cup or a glass). After disinfection, the dishes are washed with running drinking water for 1 minute per each item or kept in a container of water for 1 minute when completely immersed. Dishes made of metal are not subject to disinfection with anolyte.
- Linen is completely immersed in anolyte. The consumption rate of 5 liters per 1 kg of dry linen. After disinfection, the laundry is washed and rinsed in water.
- The toys are completely immersed in the anolyte and, after the end of the disinfection exposure, washed with running water until the smell of chlorine disappears.
- Harvesting material (rags) is completely immersed in the anolyte. After the end of disinfection exposure, the cleaning material is rinsed in water and dried.
- The disinfection quality control methodology is described in Appendix 3.
Table 1. Modes of disinfection of various objects with anolyte
| Disinfection object | Disinfection mode when | The method of disinfection | |||||
| bacterial infections (excluding tuberculosis) and viral etiology | tuberculosis | fungal infections | |||||
| active concentration chlorine% |
disinfection time, min | active concentration chlorine% |
disinfection time, min | active concentration chlorine% |
disinfection time, min | ||
| Indoor surfaces (floor, walls, hard furniture | 0,02 | 120* | 0,02 0,05 |
360 90 |
0,02 0,05 |
120 30 |
Wiping |
| Medical devices ** from: | |||||||
| - glass, metals | 0,02 | 180 | 0,05 | 30 | 0,05 | 30 | Immersion |
| - plastics, silicone rubber | 0,02 | 60 | 0,02 0,05 |
180 30 |
0,02 0,05 |
240 30 |
Immersion |
| - rubber based on natural rubber | 0,05 | 60 | 0,02 0,05 |
240 120 |
0,02 0,05 |
240 60 |
Immersion |
| Patient Care Items *** | 0,02 0,05 |
180*** 60 |
0,02 0,05 0,05 |
180*** 30*** 120 |
0,02 0,05 0,05 |
240 30*** 60 |
Immersion |
| Tableware | |||||||
| - no food residue | 0,02 | 60 | Immersion | ||||
| - with leftover food | 0,02 | 360 | 0,02 0,05 |
360 60 |
0,02 0,05 |
360 60 |
|
| Lingerie: | |||||||
| - unpolluted | 0,02 | 60 | 0,02 | 240 | Immersion | ||
| - polluted | 0,02 | 360 | 0,05 | 180 | 0,05 | 60 | |
| Toys *** | 0,02 0,05 |
180*** 60 |
0,05 | 60 | 0,05 | 60 | Immersion |
| Sanitary equipment | 0,05 | 60* | 0,05 | 120 | 0,02 0,05 |
240 30 |
Wiping |
| Harvesting material (rags) | 0,02 | 360 | 0,05 | 180 | 0,05 | 60 | Immersion |
* - Disinfection is carried out by the method of double wiping with an interval of 15 minutes The total disinfection time is indicated taking into account the 15 - minute interval between wipes.
** - To combine the process of disinfecting medical devices with the process of their pre-sterilization cleaning with anolyte (clause 1.4.) After the end of the exposure time of the anolyte specified in this table for the corresponding infectious disease, it is necessary to perform the stages of pre-sterilization cleaning (clause 4.2., Table 2) following the stage of soaking in anolyte.
*** - In addition to products made from rubber based on natural rubber.
3. APPLICATION OF ANOLITH FOR PRE-STERILIZATION CLEANING OF MEDICAL APPLICATIONS
- For pre-sterilization cleaning of medical devices, anolyte with an active chlorine concentration of 0.01% and 0.02% is used.
- Pre-sterilization cleaning is carried out manually in accordance with the following steps:
- soaking in the anolyte when the products are completely immersed in the anolyte and thoroughly filling the channels and cavities with the help of various auxiliary means (syringe, pipette, etc.);
- washing of each product in the anolyte used for soaking: the outer and accessible inner surfaces - with a cotton-gauze swab, cloth or ruff, channels - with a syringe;
- rinsing products with washing channels with running drinking water;
- rinsing products with washing channels with distilled water. - Modes of pre-sterilization cleaning of medical devices are given in table. 2, quality control - see Appendix 4.
Table 2. Modes of pre-sterilization cleaning of medical devices
| Processing object Products from: |
The concentration of active chlorine,% | Duration of the stage, min. | |||
| soaking anolyte |
washing of each product in anolyte | rinsing with running drinking water | rinsing distillation water |
||
| - glass | 0,01 | 30 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 0,5 |
| 0,02 | 20 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 0,5 | |
| - plastics | 0,02 | 20 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 0,5 |
| - metals (simplest instruments from titanium alloys) | 0,01 | 30 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 0,5 |
| 0,02 | 20 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 0,5 | |
| - rubber based on silicone rubber | 0,01 | 30 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 0,5 |
| 0,02 | 20 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 0,5 | |
| - rubber based on natural rubber | 0,01 | 30 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 0,5 |
| 0,02 | 20 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 0,5 | |
4. APPLICATION OF ANOLYTE FOR STERILIZATION OF MEDICAL PURPOSE PRODUCTS
- Sterilization of medical devices with anolyte is carried out in enameled (without damage to the enamel), glass or plastic containers, which are closed with lids, when the products are completely immersed in the anolyte, ensuring that they thoroughly fill all channels and cavities of the products. To better fill the channels with anolyte and to more completely remove air bubbles from them, use syringes, pipettes or other auxiliary means. Detachable products are immersed in the anolyte disassembled. Sterilized products should be freely placed in containers with anolyte; the thickness of the anolyte layer above the products should be at least 1 cm.
- The sterilization modes of medical devices are given in table 3.
- During sterilization (including the stage of washing products from product residues), all manipulations are performed in compliance with aseptic conditions.
- After the end of the sterilization exposure time, the products are removed with sterile forceps (forceps) from the anolyte, removing it from the channels and cavities, and transferred to a sterile container with sterile drinking water to wash the products from product residues. Washing is carried out for 1 min with complete immersion of the products in water with the filling of channels and cavities with water.
- The sterile products washed from the anolyte residues are removed from the water, placed in a sterile sheet, the remaining water in the channels is removed using a sterile syringe or other device, and the products are transferred to a sterile sterilization box lined with a sterile sheet. The shelf life of sterilized products is not more than three days.
- The containers and water used when washing sterile products from product residues are pre-sterilized by steam at a temperature of 132 ° C for 20 minutes.
Table 3. Modes of sterilization of medical devices
Annex 1. ANOLYT QUALITY CONTROL METHODS
- The quality of the anolyte is controlled by the concentration of active chlorine in the anolyte and the pH value.
- Determination of the concentration of active chlorine in the anolyte.
- Reagents used.
- Potassium iodide according to GOST 4232 h.h., 10% aqueous solution.
- Sodium sulfate (sodium thiosulfate) 5-water according to TU6 - 09-2540, 0.1 N. solution.
- Sulfuric acid according to GOST 4204, 1 N. solution.
- Soluble starch according to GOST 10163, 0.5% solution, prepared according to GOST4919.1.
- Distilled water according to GOST 6709. - Preparation for analysis.
- Preparation of a 10% potassium iodide solution. 10 g of potassium iodide are dissolved in 90 ml of freshly prepared and cooled distilled water.
- Cooking 1 n. sulfuric acid solution. 27 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid, carefully, in small portions, constantly stirring, added to 750 ml of distilled water, cooled and the volume in the volumetric flask was adjusted to 1 liter. - Analysis. In a conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 250 ml make 10 ml of anolyte, 5 ml of a 10% solution of potassium iodide and 50 ml of 1 N. sulfuric acid solution. The contents of the flask are mixed and placed in a dark place for 5 minutes. The released iodine is titrated with 0.1 n. sodium sulfate solution until light yellow in color, after which 1 ml of a 0.5% starch solution is added and the solution is titrated until the blue color disappears.
- Processing the results. Mass fraction of active chlorine X in percent is calculated by the formula
X \u003d (Y-Y1) * 0.003546 * 100/10
Where:
Y - the volume is exactly 0.1 N. a solution of sodium sulfate, spent on titration of the analyzed anolyte, cm 3;
U1 - the volume is exactly 0.1 n. sodium sulfate solution, used for titration of a control solution, cm 3;
0,003546 - the mass of chlorine corresponding to 1 cm 3 exactly 0.1 N. sodium sulfate solution, g;
10 - the mass of the analyzed samples of anolyte,
The arithmetic mean of two parallel definitions is taken as the result of the analysis. - Determination of the pH of the anolyte is carried out using the ionomer I-120.1 or "pH-150" in accordance with the instructions of the device.
Appendix 2 DISINFECTION QUALITY CONTROL METHODOLOGY
- The quality of disinfection is evaluated after it is carried out by bacteriological examination of the microbial contamination of treated objects in order to identify Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli bacteria.
- Sampling is carried out by the method of swabs.
- Surfaces (surface areas) of various objects (Section 2.2.) Are thoroughly wiped with sterile gauze wipes (wipe size 5x5 cm) moistened with a sterile neutralizer solution (0.5% sodium thiosulfate solution). After that, the napkin is placed in a sterile test tube with 10 cm 3 of the above sterile neutralizer solution and sterile glass beads, shaken for 5 minutes, avoiding wetting the cork.
- When controlling small objects (utensils, toys, etc.), washings are made from the surface of the entire object. With a large surface of objects (floors, walls, furniture, etc.), washings are made from an area of \u200b\u200bat least 100 cm 2.
- When controlling medical devices (except for products with channels and small products), washings are taken in a similar way according to the same methodology (Clause 2.1.) From the surface of the working part of the product. For products having functional channels, the working end is lowered into a sterile tube with a sterile neutralizer solution and the channel is washed 1-2 times with this solution using a sterile syringe or pipette. Small items during sampling are completely immersed in a test tube with a sterile neutralizer solution and shaken for 5 minutes. Control is subject to 1% of simultaneously processed products of the same name (but not less than three products).
- From flushing fluid (tubes with a solution of a neutralizer used in sampling), 0.1 ml inoculations are made on the surface of yolk-salt, blood agar, on Endo medium. Crops are kept in a thermostat at a temperature of 37 ° C. Results are taken into account after 48 hours.
- In the presence of colony growth on these media, the identified microorganisms are identified in accordance with the current methodological documents. In the absence of growth of microorganisms specified in paragraph 1, disinfection is considered effective.
Appendix 3 QUALITY CONTROL OF PRE-STERILIZATION CLEANING OF MEDICAL PURPOSES
- The quality of the pre-sterilization cleaning of products is assessed by placing an amidopyrine or azopyram test for the presence of residual amounts of blood according to the procedures set forth in the Methodological Instructions for Pre-Sterilization Cleaning of Medical Products, respectively (approved by the USSR Ministry of Health 08.06.82, No. 28-6 / 13) and in the guidelines "Quality control of pre-sterilization cleaning of medical devices using azopyram reagent" (approved by the USSR Ministry of Health on 05.26.88, No. 28-6 / 13).
- Control is subject to 1% of simultaneously processed products of the same name (but not less than three products).
- If blood residues are detected (positive sample), the entire group of products from which the products were taken for control should be re-processed until a negative result is obtained.

 Live journal
Live journal Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter