The use of present simpl. Present Simple - simple present tense
If we define Hpresent simple time ( present simple) a couple of phrases, it turns out that this is the time that is used if the ongoing action is ordinary, habitual, constant (regular), currently taking place.
The following are the cases in which the simple present tense should be used:
- As we already mentioned, with a normal, repetitive action.
- In sentences describing the laws and phenomena of nature, scientific results, facts, axioms.
- Expressing emotions and feelings.
- When describing everyday situations.
- Retelling a story or anecdote (list of events)
- When an action is scheduled independently of us (train schedules, cinema screenings, etc.)
| They are my brothers. | They are my brothers. |
| I jog every morning. | I run every morning. |
Conjugation of verbs in the simple present tense in English.
In general, at conjugation verbs in English change little. In simple present tense to verbs third person singular (represented by the pronouns he (he), she (she), it (it) added s.
Examples:
| to know | know |
| I know | I know |
| you know | you know / you know |
| he/she/it knows | he/she/it knows |
| we know | we know |
| you know | you know |
| they know | they know |
| to eat | there is |
| I eat | I eat |
| you eat | you eat / you eat |
| he/she/it eats | he/she/it eats |
| we eat | we eat |
| you eat | you eat |
| they eat | they are eating |
2. To go (go), to do (do)
Verbs to go (go) and to do (do) change in the third person singular. When conjugated, they are added at the end s.
she does, he does, it does
she goes, she goes, she goes
Examples:
Questions with the verb to be.
In questions with a verb to be subject and predicate change places relative to the declarative sentence, the auxiliary verb is not required.
Example:
Questions with basic verbs.
To ask a question in the present tense with main verbs, use the auxiliary verb do.
In the question do or does always placed on first place, followed by the subject and then the semantic verb.
The general scheme is as follows:
to do (in the right form) + subject + infinitive (without to)
Examples:
Questions using special question words.
Consider examples of the use of special interrogative words with the verb in questions to be:
For questions with main verbs, except for questions with to be, auxiliary verbs are always used to do. Question words where, what, what time, when, why and who precede auxiliary verbs do/does, followed by subject and semantic verb.
Examples:
Short and detailed answers with the verb "to do".
The answer to the question can be short or long. If the answer is more than one word, often use yes or no at the beginning of a sentence. If the answer is yes, there is no need to use the verb to do, but when the answer is no, its use is necessary.
Examples:
| Does he get up early? | Yes, he gets up early. |
| Does he get up early? | Yes, he gets up early. |
| No, he doesn't get up early. | |
| No, he doesn't get up early. | |
| Do you like this park? | Yes, I like this park. |
| Do you like this park? | Yes, I love this park. |
| No, I don't like this park. | |
| No, I don't like this park. |
If the answer is short yes or no lead the sentence, followed by subject and auxiliary verb to do in the correct form. This applies to how affirmative, and negative offers.
Examples:
| Does she jog every day? | Yes, she does. / No, she doesn't. | |
| Does she run every day? | Not really. | |
| Does he go to the park in the morning? | Yes, he does. / No, he doesn't. | |
| Does he go to the park in the morning? | Not really. | |
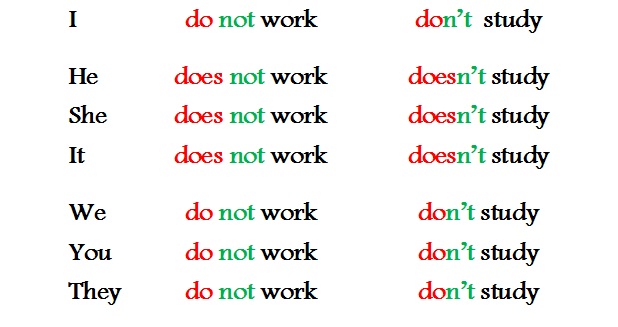
Negative with basic verbs in the simple present tense.
For education negative form in simple present tense all verbs in English (except to be) require an auxiliary verb do+not. .
Main verbs that require the presence of to do as an auxiliary do not change themselves when negated, that is, the ending s (es) is not required. When conjugated, only the auxiliary verb changes. The scheme is as follows:
subject + to do (in the right form) + not + infinitive (without to).
Examples:
Abbreviations apply:
Do+not=don"t
does+not=doesn"t
Examples:
Negation to be needs to be added not.
Examples:
I "m not a supervisor. I am not a controller.
She is not from Canada. She is not from Canada. Use the appropriate auxiliary verb in the following questions.
present simple is one of the basic tenses of English grammar. It is impossible to do without it either in writing, or especially in oral speech. In many sources you can find a variety of ridiculous phrases that this is one of the simplest times in English. Where there! Time is very difficult both in education and in proper use. There are so many nuances and a lot of all sorts of "buts" ... However, without being too lazy and reading this post to the end, you will familiarize yourself with all the intricacies of using present simple. Good luck! You can also find in Present Simple.
The use of Present Simple.
present simple used to refer to or express:
- Permanent characteristics of personality.
She speaks fluent Japanese. – She speaks Japanese fluently.
- Fact
They live in Kongo. - They live in the Congo.
- repetitive action
The Ivanovs go to Turkey every summer. The Ivanovs go to Turkey every summer.
- Absolute truths or laws of nature
Snow melts at O degrees. - Snow melts at 0 degrees.
Special cases of using Present Simple instead of Present Continuous.
- In announcements, expressions of consent
I declare our meeting open. I declare our meeting open.
- To express a sequence of actions
Now watch: I take some potatoes, peel them and carefully cut them into pieces. “Look, I take a potato, peel it and carefully cut it into pieces.
- To denote states, actions and processes expressed by verbs that do not have the Present Continuous form
Who does this truck belong to? Who owns this truck?
See more
Special cases of using Present Simple instead of Future Simple.
- To indicate an action planned for the future (more often with verbs denoting movement, and if time is indicated)
I fly to Madrid next Friday. I am flying to Madrid next Friday.
- In the clause of type I conditional sentences after the conjunctions If, when, after, until, before, unless, provided, etc.
Get me know, if they come. Let me know if they come.
Special cases of using Present Simple instead of Past Simple.
- In the headlines of periodicals
Little boy saves his mother! The little boy saved his mother.
- In descriptions for films, books, theatrical productions.
The main hero meets a young lady. They fall in love with each other. The main character met a young girl. They fell in love with each other.
- In colloquial speech, in order to more vividly and vividly convey the events that have occurred.
Yesterday I came home late. And there – who do you think I see? Mary! My sweetheart! I rush to her and kiss her! And - Yesterday I came home late - and who do you think I saw there? Mary! My dear!
- In colloquial speech with the verbs be told, hear, forget.
I am told he got a driving license last week. I was told that he got his license last week.
I hear you are leaving for Rome. “I heard you are going to Rome.
Education Present Simple.
Present Simple in affirmative sentences.
In affirmative sentences form present simple coincides with the stem of the verb in all persons, except for the 3rd person singular, where the ending -s \ es is added. Read more about the rules for adding an ending here.
Present Simple in negative sentences.
Negative sentences formed according to the scheme
do not (don't) + verb stem
does not (doesn't) + verb stem (for 3rd person singular)

Present Simple in interrogative sentences.
Interrogative sentences formed according to the scheme
Do + S (subject) + verb stem
Does + S (subject) + verb stem

I suggest you practice using
Present Simple (Presentation simpl) is a simple present tense - a very common, very important form of the English verb. It is used to convey permanent actions, as well as actions of a periodically recurring nature, to describe habits, hobbies, facts.
And although the very name of this time includes the word "simple", in application it turns out to be not so simple, there are some nuances and exceptions to the rules.
Hear how Anna Cambridge University Press explains the uses of Present Simple. Anna speaks English, but very clearly, even a beginner will understand her, especially since the explanation is accompanied by writing and pictures.
Rules for using Present Simple (video in English)
Education Table Present Simple
The table shows that only the verbs of the 3rd person singular, that is, those that agree with the pronouns he, she, it
, differ in spelling: they take the ending -s
. In some cases, this ending can be -es (go - go es, do - does, search - searches, wash - washes),
or -ies (cry - cr ies , study - studies , hurry - hurries , apply - applies ).
Examples (suggestions) + explanation in Russian
1. Verbs in present simpl are used to express action permanent or recurring:

2. We are talking about facts, for example, that the earth revolves around the sun, water boils at 100 degrees, and the like.

3. We talk about how often we do something (we use adverbs always, never, sometimes, often, rarely, usually)

4. By the way, there is a way to just remember these, this will help us .... dinosaur, or rather an acronym DINOSAUR(each letter of the word is associated with a certain adverb, thus helping to remember them)

5. We talk about our thoughts, express feelings, which, although they are temporary, are not used in, this state verbs, as well as verbs that describe our promises, assumptions, advice, namely:
suggest, advise, promise, agree, refuse, insist, apologise, recommend, want, understand

Listen to a fun, simple song for kids about the activities we do every morning when we wake up. Adults also do not hurt to listen to strengthen the use of Present Simple.
To speak English means to open many doors for yourself. In the modern world, this skill is highly valued, and therefore, learning English should be given a lot of time. It is necessary to develop such an ability in oneself from childhood, although an adult can master a new language even in the absence of any initial knowledge. The main thing is to know the grammar, and the rest will come with practice.
Everyone who is familiar with the basics of the English language has come across its tenses. It is on them that the entire grammar of English is based, and it is they that cause difficulties and problems in learning for many. The most used among tenses is the simple (indefinite) present tense (Present Simple). The table, as a rule, greatly simplifies the process of studying.
When is the Present Simple used?
English, like any language, is built on general principles and rules, which often do not allow alternatives in the application of certain grammatical structures. Some cases oblige to use only the table of use of this time must be observed for literate speech.
Present Simple is used in the following cases:
- When it comes to general rules, truths are about what everyone knows: a description of laws, natural phenomena, research results and any other generally accepted facts (Mouses love cheese - Mice love cheese).
- When we show emotions, feelings or state (I believe in love - I believe in love).
- When describing everyday or permanent situations (His parents live in Russia - His parents live in Russia).
- In the context of the future tense after the words if, when, before, until, unless (I "ll stay here untill you get back - I will stay here until you return).
- When it comes to the schedule or regular activities, phenomena (I get up at 8:30 - I get up at 8:30).
- When talking about personal habits, hobbies (I like becon - I love bacon).
- When we talk about what is happening now (She is here now - She is here now).
Although Present Simple is considered one of the simplest grammatical tenses in the English language, it has several nuances that cannot be ignored, otherwise written and spoken language will be ridiculous.
Narration in Present Simple
Declarative sentences make up the bulk of our speech. In Present Simple, they are built as follows: subject + predicate (if speech is in the third person, then with the ending -s, only for the singular).

For instance:
- I read the newspaper every morning. - I read a newspaper every morning.
- He reads the newspaper every morning. - He reads a newspaper every morning.
This is important: you must not confuse the form that the third person takes in the singular tense with the plural! The ending -s should be added only to the pronouns "it", "he", "she".
Question in Present Simple
Auxiliary and special modal verbs are taken as the basis for constructing questions in Present Simple. Such sentences are built according to the following scheme: interrogative word + special auxiliary / + subject + predicate.

If different to be are used, it should be taken as the basis for constructing the question. For example:
- He is a teacher. - He is a teacher.
- He is a teacher? - Is he a teacher?
In general questions, modal verbs are used, not auxiliary ones. For instance:
- She knows how to jump into the pool. - She can jump in the pool.
- Can she jump into the pool? - Can she jump in the pool?
The verb to do has a special meaning in Present Simple, a table of its main forms is given below. If the sentence has a semantic verb, but there is no modal verb in it, then the following forms of the verb to do are used:
| I | do |
| we | do |
| they | do |
| he | does |
| she | does |
| it | does |
| you | do |
This is important: when using the does form, the ending -s is not put in the main predicate.
Negation in Present Simple
Auxiliary and special modal verbs in Present Simple, the table of forms to do in the present tense are also used to form negative sentences.

Scheme: subject + special auxiliary / modal verbs + particle not + predicate. In practice, abbreviations are often used: do not - don "t,
does not - doesn't.
For instance:
- He runs every evening. - He runs every evening.
- He doesn't run every evening. - He does not (doesn "t) run every evening.
Table in English: Present Simple
It is better to see and understand once than to read a thousand times and remain at a loss. Visual memory and general perception helps to remember the material better. Especially when it comes to basic time in English, such as Present Simple. A table for children, as well as for adults, is a great option for quickly learning grammar.
Verbs in Present Simple
All verbs are important for constructing sentences: modal, auxiliary and, of course, main. Together, they create a certain system that makes up the main part of both this tense and the entire English language.

In Present Simple, the first one is used. At the same time, there are nuances that must be taken into account when constructing a sentence of this time:
- In affirmative sentences from the third person singular, the verb acquires the particle -s.
- In denials and third person singular questions using the does form, the particle -s is not used.
- In an interrogative sentence, the auxiliary verb is used before the subject. In case of type, an interrogative pronoun is used before them.
- If the question is for the subject itself, then Who is used instead of the subject and is applied before the predicate.
The verbs in Present Simple, the conjugation table of which is given below, are a framework without which it would be impossible to express one's thoughts.
| Number | Face | Declarative sentences | Negative sentences | Interrogative sentences |
| one. | 1 | I draw. | I don't draw. | Do I draw? |
| 2 | you draw. | You don't draw. | Do you draw? | |
| 3 | He draws. | He doesn't draw. | Does he draw? Does she draw? Does it draw? |
|
| plural | 1 | You don't draw. | Do you draw? | |
| 2 | We draw. | We don't draw. | Do we draw? | |
| 3 | They draw. | They don't draw. | Do they draw? |
marker words
It is one thing to learn what the Present Simple table looks like, and another thing is to put into practice the knowledge gained. Sometimes, looking at a sentence, it is not immediately possible to determine to which grammatical tense it belongs. That is why there are words-markers - a kind of indicators of a particular time. They are usually used after a modal/special auxiliary or at the end of a sentence. Marker words for Present Simple:
- sometimes - sometimes
- regularly - constantly
- rarely - rarely
- often - often
- at the weekend - on the weekend,
- on Wednesday - on Wednesdays,
- every day - every day,
- at weekends - on weekends,
- always - always,
- at 9 o "clock - at 9 o'clock,
- usually - usually.
- Classification of explosions depending on the environment
- black prince ship balaclava
- Who is Padawan Padowan Star Wars
- What is the flag on the ship. Yellow flag on the ship. Additional signs of the code of signals of the USSR
- Anglo-Dutch rivalry
- About the war won, but unsuccessful
- Black Sea Higher Naval Order of the Red Star School named after P

 Live Journal
Live Journal Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter